Page 122 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 122
CHAPT E R 2 Introduction to Transaction Processing 93
EDIT RUN
At a predetermined time each day, the data processing department executes this batch system. The edit
program is the first to be run. This program identifies clerical errors in the batch and automatically
removes these records from the transaction file. Error records go to a separate error file, where an author-
ized person corrects and resubmits them for processing with the next day’s batch. The edit program recal-
culates the batch total to reflect changes due to the removal of error records. The resulting clean
transaction file then moves to the next program in the system.
SORT RUNS
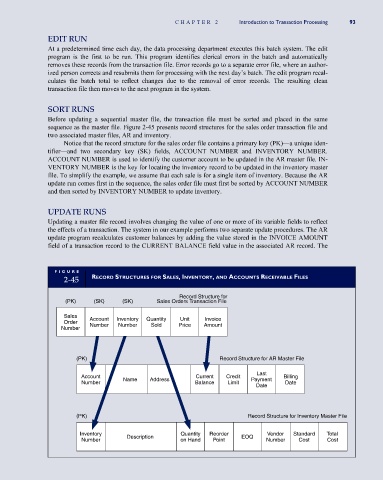
Before updating a sequential master file, the transaction file must be sorted and placed in the same
sequence as the master file. Figure 2-45 presents record structures for the sales order transaction file and
two associated master files, AR and inventory.
Notice that the record structure for the sales order file contains a primary key (PK)—a unique iden-
tifier—and two secondary key (SK) fields, ACCOUNT NUMBER and INVENTORY NUMBER.
ACCOUNT NUMBER is used to identify the customer account to be updated in the AR master file. IN-
VENTORY NUMBER is the key for locating the inventory record to be updated in the inventory master
file. To simplify the example, we assume that each sale is for a single item of inventory. Because the AR
update run comes first in the sequence, the sales order file must first be sorted by ACCOUNT NUMBER
and then sorted by INVENTORY NUMBER to update inventory.
UPDATE RUNS
Updating a master file record involves changing the value of one or more of its variable fields to reflect
the effects of a transaction. The system in our example performs two separate update procedures. The AR
update program recalculates customer balances by adding the value stored in the INVOICE AMOUNT
field of a transaction record to the CURRENT BALANCE field value in the associated AR record. The
FI G U R E
2-45 RECORD STRUCTURES FOR SALES,INVENTORY, AND ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE FILES
Record Structure for
(PK) (SK) (SK) Sales Orders Transaction File
Sales Account Inventory Quantity Unit Invoice
Order Number Number Sold Price Amount
Number
(PK) Record Structure for AR Master File
Last
Account Name Address Current Credit Payment Billing
Number Balance Limit Date
Date
(PK) Record Structure for Inventory Master File
Inventory Quantity Reorder Vendor Standard Total
Number Description on Hand Point EOQ Number Cost Cost