Page 126 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 126
CHAPT E R 2 Introduction to Transaction Processing 97
FI G U R E
2-48 SAMPLE TRANSACTIONS AND MASTER FILE RECORDS
Transaction Master
File File
(T) (M)
Order of Records Records Order of
Processing Processing
(Key) (Key)
1 Data 1 Data Updated
4 2
10 3
7 4 Updated
Not
Processed
9 5
6
7
8
9
10 Updated
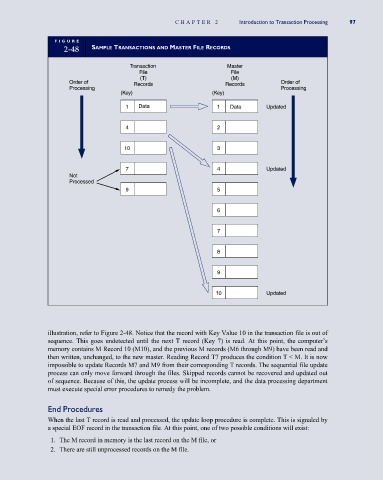
illustration, refer to Figure 2-48. Notice that the record with Key Value 10 in the transaction file is out of
sequence. This goes undetected until the next T record (Key 7) is read. At this point, the computer’s
memory contains M Record 10 (M10), and the previous M records (M6 through M9) have been read and
then written, unchanged, to the new master. Reading Record T7 produces the condition T < M. It is now
impossible to update Records M7 and M9 from their corresponding T records. The sequential file update
process can only move forward through the files. Skipped records cannot be recovered and updated out
of sequence. Because of this, the update process will be incomplete, and the data processing department
must execute special error procedures to remedy the problem.
End Procedures
When the last T record is read and processed, the update loop procedure is complete. This is signaled by
a special EOF record in the transaction file. At this point, one of two possible conditions will exist:
1. The M record in memory is the last record on the M file, or
2. There are still unprocessed records on the M file.