Page 219 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 219
190 PART II Transaction Cycles and Business Processes
performing batch control balancing after each run and by producing management reports and summaries
for end users to review.
PC-Based Accounting Systems
The software market offers hundreds of PC-based accounting systems. In contrast to mainframe and cli-
ent-server systems that are frequently custom-designed to meet the specific user requirements, PC appli-
cations tend to be general-purpose systems that serve a wide range of needs. This strategy allows
software vendors to mass-produce low-cost and error-free standard products. Not surprisingly, PC
accounting systems are popular with smaller firms, which use them to automate and replace manual sys-
tems and thus become more efficient and competitive. PC systems have also made inroads with larger
companies that have decentralized operations.
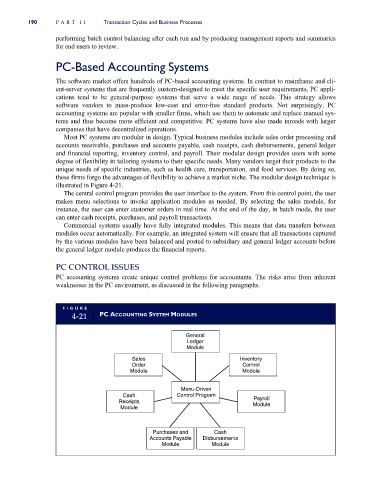
Most PC systems are modular in design. Typical business modules include sales order processing and
accounts receivable, purchases and accounts payable, cash receipts, cash disbursements, general ledger
and financial reporting, inventory control, and payroll. Their modular design provides users with some
degree of flexibility in tailoring systems to their specific needs. Many vendors target their products to the
unique needs of specific industries, such as health care, transportation, and food services. By doing so,
these firms forgo the advantages of flexibility to achieve a market niche. The modular design technique is
illustrated in Figure 4-21.
The central control program provides the user interface to the system. From this control point, the user
makes menu selections to invoke application modules as needed. By selecting the sales module, for
instance, the user can enter customer orders in real time. At the end of the day, in batch mode, the user
can enter cash receipts, purchases, and payroll transactions.
Commercial systems usually have fully integrated modules. This means that data transfers between
modules occur automatically. For example, an integrated system will ensure that all transactions captured
by the various modules have been balanced and posted to subsidiary and general ledger accounts before
the general ledger module produces the financial reports.
PC CONTROL ISSUES
PC accounting systems create unique control problems for accountants. The risks arise from inherent
weaknesses in the PC environment, as discussed in the following paragraphs.
FI GU RE
4-21 PC ACCOUNTING SYSTEM MODULES
General
Ledger
Module
Sales Inventory
Order Control
Module Module
Menu-Driven
Cash Control Program Payroll
Receipts Module
Module
Purchases and Cash
Accounts Payable Disbursements
Module Module