Page 315 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 315
286 PART II Transaction Cycles and Business Processes
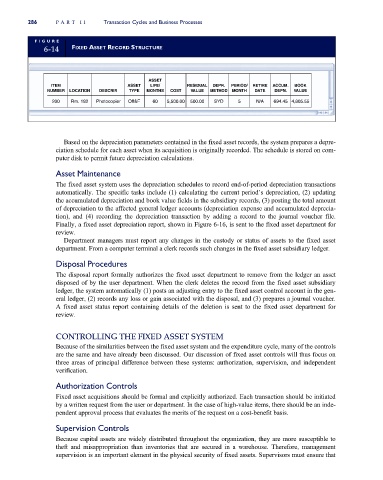
FI G U RE
6-14 FIXED ASSET RECORD STRUCTURE
ASSET
ITEM ASSET LIFE/ RESIDUAL DEPR. PERIOD/ RETIRE ACCUM. BOOK
NUMBER LOCATION DESCRIP. TYPE MONTHS COST VALUE METHOD MONTH DATE DEPN. VALUE
200 Rm. 182 Photocopier Off&F 60 5,500.00 500.00 SYD 5 N/A 694.45 4,805.55
Based on the depreciation parameters contained in the fixed asset records, the system prepares a depre-
ciation schedule for each asset when its acquisition is originally recorded. The schedule is stored on com-
puter disk to permit future depreciation calculations.
Asset Maintenance
The fixed asset system uses the depreciation schedules to record end-of-period depreciation transactions
automatically. The specific tasks include (1) calculating the current period’s depreciation, (2) updating
the accumulated depreciation and book value fields in the subsidiary records, (3) posting the total amount
of depreciation to the affected general ledger accounts (depreciation expense and accumulated deprecia-
tion), and (4) recording the depreciation transaction by adding a record to the journal voucher file.
Finally, a fixed asset depreciation report, shown in Figure 6-16, is sent to the fixed asset department for
review.
Department managers must report any changes in the custody or status of assets to the fixed asset
department. From a computer terminal a clerk records such changes in the fixed asset subsidiary ledger.
Disposal Procedures
The disposal report formally authorizes the fixed asset department to remove from the ledger an asset
disposed of by the user department. When the clerk deletes the record from the fixed asset subsidiary
ledger, the system automatically (1) posts an adjusting entry to the fixed asset control account in the gen-
eral ledger, (2) records any loss or gain associated with the disposal, and (3) prepares a journal voucher.
A fixed asset status report containing details of the deletion is sent to the fixed asset department for
review.
CONTROLLING THE FIXED ASSET SYSTEM
Because of the similarities between the fixed asset system and the expenditure cycle, many of the controls
are the same and have already been discussed. Our discussion of fixed asset controls will thus focus on
three areas of principal difference between these systems: authorization, supervision, and independent
verification.
Authorization Controls
Fixed asset acquisitions should be formal and explicitly authorized. Each transaction should be initiated
by a written request from the user or department. In the case of high-value items, there should be an inde-
pendent approval process that evaluates the merits of the request on a cost-benefit basis.
Supervision Controls
Because capital assets are widely distributed throughout the organization, they are more susceptible to
theft and misappropriation than inventories that are secured in a warehouse. Therefore, management
supervision is an important element in the physical security of fixed assets. Supervisors must ensure that