Page 42 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 42
C H A P TER 1 The Information System: An Accountant’s Perspective 13
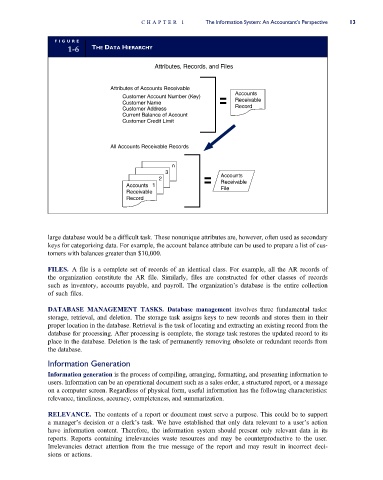
FI G U R E
1-6 THE DATA HIERARCHY
Attributes, Records, and Files
Attributes of Accounts Receivable
Accounts
Customer Account Number (Key)
Customer Name Receivable
Customer Address Record
Current Balance of Account
Customer Credit Limit
All Accounts Receivable Records
n
3
2 Accounts
Accounts 1 Receivable
File
Receivable
Record
large database would be a difficult task. These nonunique attributes are, however, often used as secondary
keys for categorizing data. For example, the account balance attribute can be used to prepare a list of cus-
tomers with balances greater than $10,000.
FILES. A file is a complete set of records of an identical class. For example, all the AR records of
the organization constitute the AR file. Similarly, files are constructed for other classes of records
such as inventory, accounts payable, and payroll. The organization’s database is the entire collection
of such files.
DATABASE MANAGEMENT TASKS. Database management involves three fundamental tasks:
storage, retrieval, and deletion. The storage task assigns keys to new records and stores them in their
proper location in the database. Retrieval is the task of locating and extracting an existing record from the
database for processing. After processing is complete, the storage task restores the updated record to its
place in the database. Deletion is the task of permanently removing obsolete or redundant records from
the database.
Information Generation
Information generation is the process of compiling, arranging, formatting, and presenting information to
users. Information can be an operational document such as a sales order, a structured report, or a message
on a computer screen. Regardless of physical form, useful information has the following characteristics:
relevance, timeliness, accuracy, completeness, and summarization.
RELEVANCE. The contents of a report or document must serve a purpose. This could be to support
a manager’s decision or a clerk’s task. We have established that only data relevant to a user’s action
have information content. Therefore, the information system should present only relevant data in its
reports. Reports containing irrelevancies waste resources and may be counterproductive to the user.
Irrelevancies detract attention from the true message of the report and may result in incorrect deci-
sions or actions.