Page 71 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 71
42 PART I Overview of Accounting Information Systems
An Overview of Transaction Processing
TPS applications process financial transactions. A financial transaction was defined in Chapter 1 as
An economic event that affects the assets and equities of the firm, is reflected in its accounts, and is
measured in monetary terms.
The most common financial transactions are economic exchanges with external parties. These include
the sale of goods or services, the purchase of inventory, the discharge of financial obligations, and the
receipt of cash on account from customers. Financial transactions also include certain internal events such
as the depreciation of fixed assets; the application of labor, raw materials, and overhead to the production
process; and the transfer of inventory from one department to another.
Financial transactions are common business events that occur regularly. For instance, thousands of
transactions of a particular type (sales to customers) may occur daily. To deal efficiently with such vol-
ume, business firms group similar types of transactions into transaction cycles.
TRANSACTION CYCLES
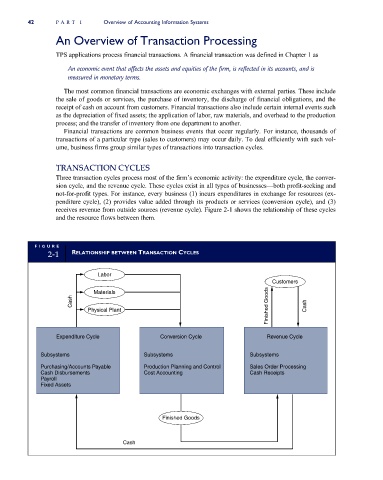
Three transaction cycles process most of the firm’s economic activity: the expenditure cycle, the conver-
sion cycle, and the revenue cycle. These cycles exist in all types of businesses—both profit-seeking and
not-for-profit types. For instance, every business (1) incurs expenditures in exchange for resources (ex-
penditure cycle), (2) provides value added through its products or services (conversion cycle), and (3)
receives revenue from outside sources (revenue cycle). Figure 2-1 shows the relationship of these cycles
and the resource flows between them.
FI G U RE
2-1 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TRANSACTION CYCLES
Labor
Customers
Materials
Cash Finished Goods Cash
Physical Plant
Expenditure Cycle Conversion Cycle Revenue Cycle
Subsystems Subsystems Subsystems
Purchasing/Accounts Payable Production Planning and Control Sales Order Processing
Cash Disbursements Cost Accounting Cash Receipts
Payroll
Fixed Assets
Finished Goods
Cash