Page 217 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 217
208 3. NOISE IN MARINE SEISMICS
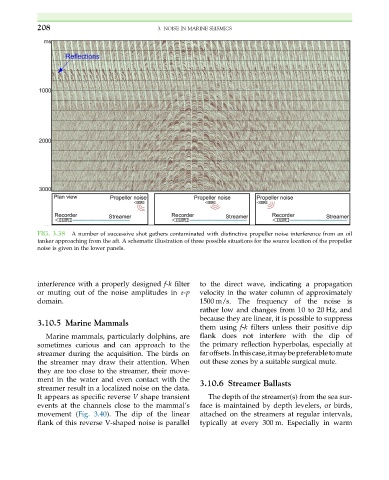
FIG. 3.38 A number of successive shot gathers contaminated with distinctive propeller noise interference from an oil
tanker approaching from the aft. A schematic illustration of three possible situations for the source location of the propeller
noise is given in the lower panels.
interference with a properly designed f-k filter to the direct wave, indicating a propagation
or muting out of the noise amplitudes in τ-p velocity in the water column of approximately
domain. 1500 m/s. The frequency of the noise is
rather low and changes from 10 to 20 Hz, and
because they are linear, it is possible to suppress
3.10.5 Marine Mammals
them using f-k filters unless their positive dip
Marine mammals, particularly dolphins, are flank does not interfere with the dip of
sometimes curious and can approach to the the primary reflection hyperbolas, especially at
streamer during the acquisition. The birds on faroffsets.Inthiscase,itmaybepreferabletomute
the streamer may draw their attention. When out these zones by a suitable surgical mute.
they are too close to the streamer, their move-
ment in the water and even contact with the 3.10.6 Streamer Ballasts
streamer result in a localized noise on the data.
It appears as specific reverse V shape transient The depth of the streamer(s) from the sea sur-
events at the channels close to the mammal’s face is maintained by depth levelers, or birds,
movement (Fig. 3.40). The dip of the linear attached on the streamers at regular intervals,
flank of this reverse V-shaped noise is parallel typically at every 300 m. Especially in warm