Page 221 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 221
212 4. FUNDAMENTALS OF DATA PROCESSING
possible to transform the data from the time or of an event in the seismic data from the zero mag-
distance domain to the frequency domain by nitude axis. Period is defined as recurrence time
spectral analysis. Because some of the mathe- of a continuous signal observed in the time
matical processes can be performed much more domain. In seismic exploration, the unit of the
easily on the frequency components of a time period is seconds. It is represented by T,and
domain signal, time and frequency domains is inversely proportional to the frequency as
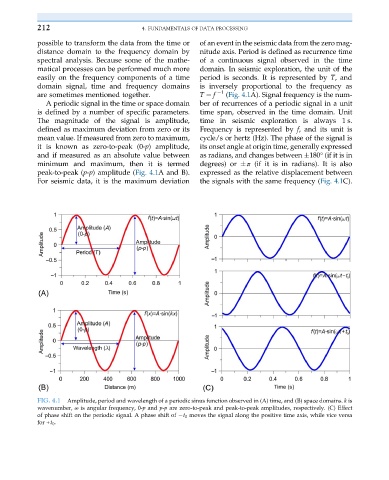
are sometimes mentioned together. T ¼ f 1 (Fig. 4.1A). Signal frequency is the num-
A periodic signal in the time or space domain ber of recurrences of a periodic signal in a unit
is defined by a number of specific parameters. time span, observed in the time domain. Unit
The magnitude of the signal is amplitude, time in seismic exploration is always 1 s.
defined as maximum deviation from zero or its Frequency is represented by f, and its unit is
mean value. If measured from zero to maximum, cycle/s or hertz (Hz). The phase of the signal is
it is known as zero-to-peak (0-p) amplitude, its onset angle at origin time, generally expressed
andifmeasuredas an absolute value between as radians, and changes between 180° (if it is in
minimum and maximum, then it is termed degrees) or π (if it is in radians). It is also
peak-to-peak (p-p) amplitude (Fig. 4.1Aand B). expressed as the relative displacement between
For seismic data, it is the maximum deviation the signals with the same frequency (Fig. 4.1C).
FIG. 4.1 Amplitude, period and wavelength of a periodic sinus function observed in (A) time, and (B) space domains. k is
wavenumber, ω is angular frequency, 0-p and p-p are zero-to-peak and peak-to-peak amplitudes, respectively. (C) Effect
of phase shift on the periodic signal. A phase shift of t 0 moves the signal along the positive time axis, while vice versa
for +t 0 .