Page 218 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 218
3.10 OTHER NOISE TYPES 209
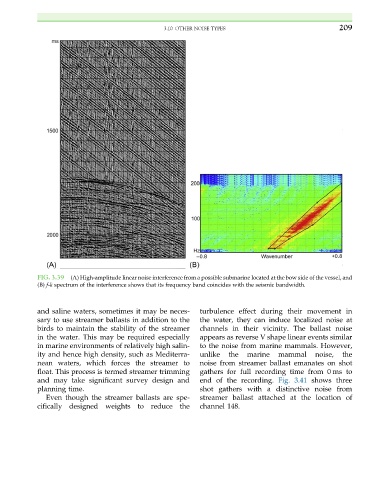
FIG. 3.39 (A) High-amplitude linear noise interference from a possible submarine located at the bow side of the vessel, and
(B) f-k spectrum of the interference shows that its frequency band coincides with the seismic bandwidth.
and saline waters, sometimes it may be neces- turbulence effect during their movement in
sary to use streamer ballasts in addition to the the water, they can induce localized noise at
birds to maintain the stability of the streamer channels in their vicinity. The ballast noise
in the water. This may be required especially appears as reverse V shape linear events similar
in marine environments of relatively high salin- to the noise from marine mammals. However,
ity and hence high density, such as Mediterra- unlike the marine mammal noise, the
nean waters, which forces the streamer to noise from streamer ballast emanates on shot
float. This process is termed streamer trimming gathers for full recording time from 0 ms to
and may take significant survey design and end of the recording. Fig. 3.41 shows three
planning time. shot gathers with a distinctive noise from
Even though the streamer ballasts are spe- streamer ballast attached at the location of
cifically designed weights to reduce the channel 148.