Page 223 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 223
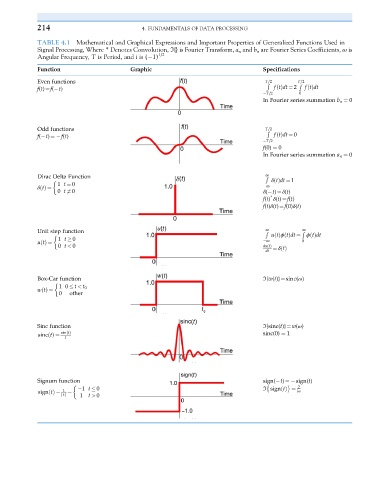
214 4. FUNDAMENTALS OF DATA PROCESSING
TABLE 4.1 Mathematical and Graphical Expressions and Important Properties of Generalized Functions Used in
Signal Processing, Where * Denotes Convolution, ℑ{} is Fourier Transform, a n and b n are Fourier Series Coefficients, ω is
Angular Frequency, T is Period, and i is ( 1) 1/2
Function Graphic Specifications
Even functions T=2 T=2
R R
f(t)¼f( t) ftðÞdt ¼ 2 ftðÞdt
T=2 0
In Fourier series summation b n ¼ 0
Odd functions T=2
R
f( t)¼ f(t) ftðÞdt ¼ 0
T=2
f(0) ¼ 0
In Fourier series summation a n ¼ 0
Dirac Delta Function R ∞
δ tðÞdt ¼ 1
1 t ¼ 0 ∞
δ tðÞ ¼
0 t 6¼ 0 δ( t)¼δ(t)
∗
f(t) δ(t)¼f(t)
f(t)δ(t)¼f(0)δ(t)
Unit step function R ∞ R ∞
utðÞϕ tðÞdt ¼ ϕ tðÞdt
1 t 0 ∞ 0
utðÞ ¼
0 t < 0 du tðÞ
dt ¼ δ tðÞ
Box-Car function ℑ{w(t)}¼sinc(ω)
10 t < t 0
wtðÞ ¼
0 other
Sinc function ℑ{sinc(t)}¼w(ω)
sin tðÞ sinc(0) ¼ 1
sinc tðÞ ¼
t
Signum function sign( t)¼ sign(t)
2
1 t 0 ℑ sign tðÞ ¼
1 iω
sign tðÞ ¼ ¼
t jj 1 t > 0