Page 297 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 297
288 5. PREPROCESSING
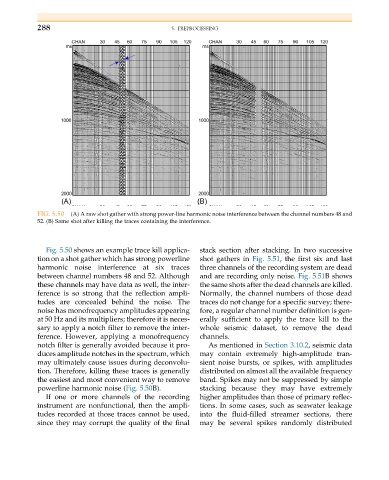
FIG. 5.50 (A) A raw shot gather with strong power-line harmonic noise interference between the channel numbers 48 and
52. (B) Same shot after killing the traces containing the interference.
Fig. 5.50 shows an example trace kill applica- stack section after stacking. In two successive
tion on a shot gather which has strong powerline shot gathers in Fig. 5.51, the first six and last
harmonic noise interference at six traces three channels of the recording system are dead
between channel numbers 48 and 52. Although and are recording only noise. Fig. 5.51B shows
these channels may have data as well, the inter- the same shots after the dead channels are killed.
ference is so strong that the reflection ampli- Normally, the channel numbers of those dead
tudes are concealed behind the noise. The traces do not change for a specific survey; there-
noise has monofrequency amplitudes appearing fore, a regular channel number definition is gen-
at 50 Hz and its multipliers; therefore it is neces- erally sufficient to apply the trace kill to the
sary to apply a notch filter to remove the inter- whole seismic dataset, to remove the dead
ference. However, applying a monofrequency channels.
notch filter is generally avoided because it pro- As mentioned in Section 3.10.2, seismic data
duces amplitude notches in the spectrum, which may contain extremely high-amplitude tran-
may ultimately cause issues during deconvolu- sient noise bursts, or spikes, with amplitudes
tion. Therefore, killing these traces is generally distributed on almost all the available frequency
the easiest and most convenient way to remove band. Spikes may not be suppressed by simple
powerline harmonic noise (Fig. 5.50B). stacking because they may have extremely
If one or more channels of the recording higher amplitudes than those of primary reflec-
instrument are nonfunctional, then the ampli- tions. In some cases, such as seawater leakage
tudes recorded at those traces cannot be used, into the fluid-filled streamer sections, there
since they may corrupt the quality of the final may be several spikes randomly distributed