Page 68 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 68
2.1 COMPONENTS OF MARINE SEISMIC ACQUISITION 59
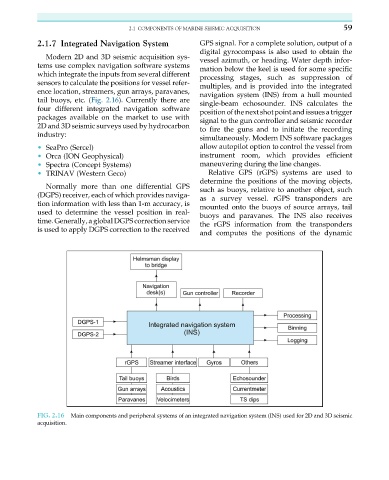
2.1.7 Integrated Navigation System GPS signal. For a complete solution, output of a
digital gyrocompass is also used to obtain the
Modern 2D and 3D seismic acquisition sys- vessel azimuth, or heading. Water depth infor-
tems use complex navigation software systems mation below the keel is used for some specific
which integrate the inputs from several different processing stages, such as suppression of
sensors to calculate the positions for vessel refer- multiples, and is provided into the integrated
ence location, streamers, gun arrays, paravanes,
navigation system (INS) from a hull mounted
tail buoys, etc. (Fig. 2.16). Currently there are single-beam echosounder. INS calculates the
four different integrated navigation software position of the next shotpoint and issues atrigger
packages available on the market to use with signal to the gun controller and seismic recorder
2D and 3D seismic surveys used by hydrocarbon to fire the guns and to initiate the recording
industry:
simultaneously. Modern INS software packages
• SeaPro (Sercel) allow autopilot option to control the vessel from
• Orca (ION Geophysical) instrument room, which provides efficient
• Spectra (Concept Systems) maneuvering during the line changes.
• TRINAV (Western Geco) Relative GPS (rGPS) systems are used to
determine the positions of the moving objects,
Normally more than one differential GPS
such as buoys, relative to another object, such
(DGPS) receiver, each of which provides naviga-
as a survey vessel. rGPS transponders are
tion information with less than 1-m accuracy, is
mounted onto the buoys of source arrays, tail
used to determine the vessel position in real-
buoys and paravanes. The INS also receives
time. Generally, a global DGPS correction service
the rGPS information from the transponders
is used to apply DGPS correction to the received
and computes the positions of the dynamic
FIG. 2.16 Main components and peripheral systems of an integrated navigation system (INS) used for 2D and 3D seismic
acquisition.