Page 261 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 261
246 CARBON NANOTUBES, PILLARED CLAYS, AND POLYMERIC RESINS
300
Amount of benzene adsorbed (mg/g) 200
250
150
100
50
SWNTs as-prepared
HNO 3 -treated
0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
p/p o
◦
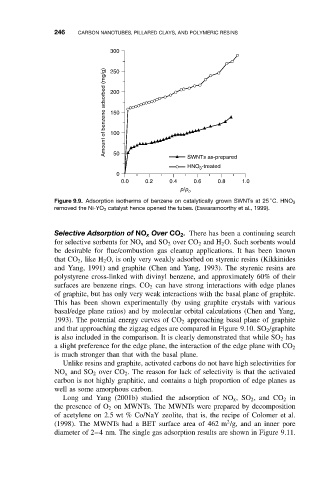
Figure 9.9. Adsorption isotherms of benzene on catalytically grown SWNTs at 25 C. HNO 3
removed the Ni-YO 3 catalyst hence opened the tubes. (Eswaramoorthy et al., 1999).
Selective Adsorption of NO x Over CO 2 . There has been a continuing search
for selective sorbents for NO x and SO 2 over CO 2 and H 2 O. Such sorbents would
be desirable for flue/combustion gas cleanup applications. It has been known
that CO 2 , like H 2 O, is only very weakly adsorbed on styrenic resins (Kikkinides
and Yang, 1991) and graphite (Chen and Yang, 1993). The styrenic resins are
polystyrene cross-linked with divinyl benzene, and approximately 60% of their
surfaces are benzene rings. CO 2 can have strong interactions with edge planes
of graphite, but has only very weak interactions with the basal plane of graphite.
This has been shown experimentally (by using graphite crystals with various
basal/edge plane ratios) and by molecular orbital calculations (Chen and Yang,
1993). The potential energy curves of CO 2 approaching basal plane of graphite
and that approaching the zigzag edges are compared in Figure 9.10. SO 2 /graphite
is also included in the comparison. It is clearly demonstrated that while SO 2 has
a slight preference for the edge plane, the interaction of the edge plane with CO 2
is much stronger than that with the basal plane.
Unlike resins and graphite, activated carbons do not have high selectivities for
NO x and SO 2 over CO 2 . The reason for lack of selectivity is that the activated
carbon is not highly graphitic, and contains a high proportion of edge planes as
well as some amorphous carbon.
Long and Yang (2001b) studied the adsorption of NO x ,SO 2 ,and CO 2 in
the presence of O 2 on MWNTs. The MWNTs were prepared by decomposition
of acetylene on 2.5 wt % Co/NaY zeolite, that is, the recipe of Colomer et al.
2
(1998). The MWNTs had a BET surface area of 462 m /g, and an inner pore
diameter of 2–4 nm. The single gas adsorption results are shown in Figure 9.11.