Page 324 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 324
HYDROGEN STORAGE 309
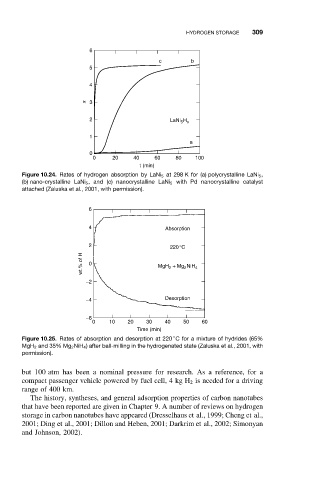
6
c b
5
4
x 3
2
LaNi 5 H x
1
a
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
t (min)
Figure 10.24. Rates of hydrogen absorption by LaNi 5 at 298 K for (a) polycrystalline LaNi 5 ,
(b) nano-crystalline LaNi 5 , and (c) nanocrystalline LaNi 5 with Pd nanocrystalline catalyst
attached (Zaluska et al., 2001, with permission).
6
4 Absorption
2
220°C
wt.% of H 0 MgH 2 + Mg 2 NiH 4
−2
−4 Desorption
−6
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Time (min)
◦
Figure 10.25. Rates of absorption and desorption at 220 C for a mixture of hydrides (65%
MgH 2 and 35% Mg 2 NiH 4 ) after ball-milling in the hydrogenated state (Zaluska et al., 2001, with
permission).
but 100 atm has been a nominal pressure for research. As a reference, for a
compact passenger vehicle powered by fuel cell, 4 kg H 2 is needed for a driving
range of 400 km.
The history, syntheses, and general adsorption properties of carbon nanotubes
that have been reported are given in Chapter 9. A number of reviews on hydrogen
storage in carbon nanotubes have appeared (Dresselhaus et al., 1999; Cheng et al.,
2001; Ding et al., 2001; Dillon and Heben, 2001; Darkrim et al., 2002; Simonyan
and Johnson, 2002).