Page 51 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 51
48 Fundamentals of adsorption equilibria
0
o -1 ---
0
B
-2 --
I ...... I I
0 10 20 30
E:2X 10 -6
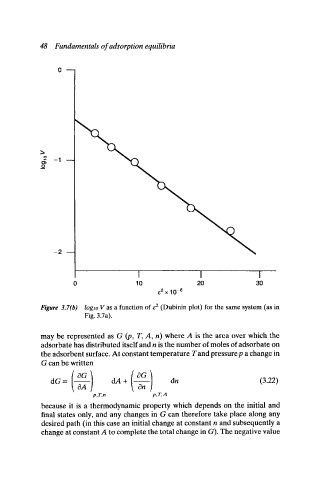
Figure 3.7(b) logto V as a function of e 2 (Dubinin plot) for the same system (as in
Fig. 3.7a).
may be represented as G (p, T, A, n) where A is the area over which the
adsorbate has distributed itself and n is the number of moles of adsorbate on
the adsorbent surface. At constant temperature T and pressure p a change in
G can be written
OG dA + dn (3.22)
dG = 0.4 On
( t
p,T,n p,T,A
because it is a thermodynamic property which depends on the initial and
final states only, and any changes in G can therefore take place along any
desired path (in this case an initial change at constant n and subsequently a
change at constant A to complete the total change in G). The negative value