Page 82 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 82
Rates of adsorption of gases and vapours by porous media 79
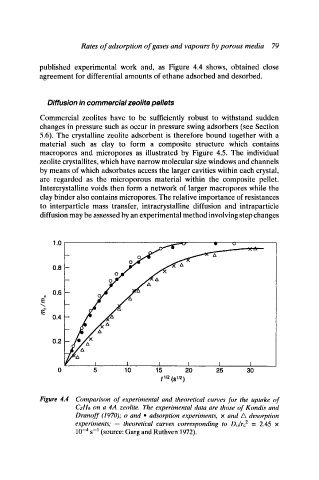
published experimental work and, as Figure 4.4 shows, obtained close
agreement for differential amounts of ethane adsorbed and desorbed.
Diffusion in commercial zeofite pellets
Commercial zeolites have to be sufficiently robust to withstand sudden
changes in pressure such as occur in pressure swing adsorbers (see Section
5.6). The crystalline zeolite adsorbent is therefore bound together with a
material such as clay to form a composite structure which contains
macropores and micropores as illustrated by Figure 4.5. The individual
zeolite crystallites, which have narrow molecular size windows and channels
by means of which adsorbates access the larger cavities within each crystal,
are regarded as the microporous material within the composite pellet.
Intercrystalline voids then form a network of larger macropores while the
clay binder also contains micropores. The relative importance of resistances
to interparticle mass transfer, intracrystalline diffusion and intraparticle
diffusion may be assessed by an experimental method involving step changes
1.0
0.8
0.6
E
0.4
0.2
f
_t ...... I I ........... I , ,I I
5 10 15 20 25 30
t v2 (SV2)
Figure 4.4 Comparison of experimental and theoretical curves for the uptake of
(721-16 on a 4A zeolite. The experimental data are those of Kondis and
Dranoff (1970); o and i adsorption experiments, x and A desorption
experiments; - theoretical curves corresponding to Do~re 2 = 2.45 x
10 -4 s -1 (source: Garg and Ruthven 1972).