Page 90 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 90
Rates of adsorption of gases and vapours by porous media 87
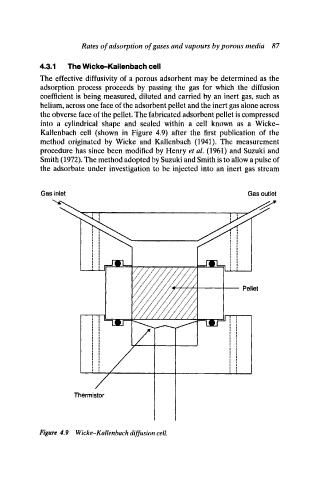
4.3.1 The Wicke-Kallenbach cell
The effective diffusivity of a porous adsorbent may be determined as the
adsorption process proceeds by passing the gas for which the diffusion
coefficient is being measured, diluted and carried by an inert gas, such as
helium, across one face of the adsorbent pellet and the inert gas alone across
the obverse face of the pellet. The fabricated adsorbent pellet is compressed
into a cylindrical shape and sealed within a cell known as a Wicke-
Kallenbach cell (shown in Figure 4.9) after the first publication of the
method originated by Wicke and Kallenbach (1941). The measurement
procedure has since been modified by Henry et al. (1961) and Suzuki and
Smith (1972). The method adopted by Suzuki and Smith is to allow a pulse of
the adsorbate under investigation to be injected into an inert gas stream
Gas inlet Gas outlet
I I I I
t I
I I I I
I I
I I
I I
I I
I I
I I
I I
I I
I= I
_ ! | i
Pellet
I I I I
I I I I
I I
I I
I I
I I I I
I I I I
I I
I I
I I
I I I I
I I
I I
I I I I
I I
I I
Thermistor
Figure 4.9 Wicke-Kallenbach diffusion cell.