Page 31 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 31
Else_AIEC-INGLE_Ch001.qxd 7/13/2006 1:53 PM Page 27
1.3 T reatment Methods 27
energy sector, are the most important sources of air pollutants. In the case of w ater bodies,
vious that agriculture and the metal industry, it is ob plus the acti vities in the production of
inorganic chemicals and fertilizers, constitute the major polluters.
1.3 TREATMENT METHODS
The minimization of the releases into the environment can be largely achie ed by v
• pollution prevention measures
• waste treatment (end-of-pipe techniques).
The first approach may inolve cleaner synthesis processes, improrec v, v ed technology y-
ed use of catalysts,
v
cling of residues, impro and generally e , grated into ery technique inte v
the process that leads to less w aste; whereas the second one is an end-of-pipe treatment of
the waste that is inevitably produced by a chemical process. Both approaches have to be com-
bined so that our releases into the environment are as minimal and harmless as possible.
Waste-treatment techniques are classified by the type of contaminant. The main tech-
niques concerning waste gas treatment are the follo wing.
VOCs and inorganic compounds : membrane separation, condensation, adsorption , wet
scrubbing, biof bioscrubbing, biotrickling, thermal oxidation, catalytic oxidation,
iltration,
and flaring.
,
yclone,
Particulate matter : separator c electrostatic precipitator wet dust scrubber f , , ab-
iltration,
ilter
ilter ric f, catalytic f two-stage dust f absolute f high-efy air f , ilter icienc f , ilter
,
and mist f. ilter
Gaseous pollutants in combustion exhaust gases : dry sorbent injection, semidry sorbent
injection, wet sorbent injection, selecti e noncatalytic reduction of NO v x (SNCR), selecti e v
catalytic reduction of NO x (SCR).
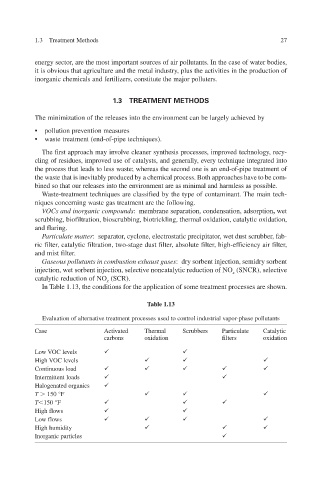
In Table 1.13, the conditions for the application of some treatment processes are sho wn.
Table 1.13
Evaluation of alternative treatment processes used to control industrial v apor -phase pollutants
Case Activated Thermal Scrubbers Particulate Catalytic
carbons oxidation filters oxidation
Low VOC levels
High VOC levels
Continuous load
Intermittent loads
ganics Halogenated or
T 150 °F
T 150 °F
High flows
Low flows
High humidity
Inorganic particles