Page 67 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 67
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:44 PM Page 63
3.1 Introduction to Heterogeneous Processes 63
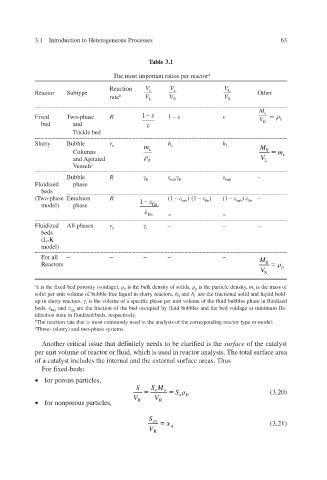
Table 3.1
The most important ratios per reactor a
Reaction V V V
L
Reactor Subtype s s Other
rate b V L V R V R
1 M s
Fixed Two-phase R 1 – b
V
bed and R
Trickle bed
Slurry Bubble r h h
u m s L M
Columns s S m s
and Agitated p V L
Vessels c
Bubble R –
b bub b bub
Fluidized phase
beds
(Two-phase Emulsion R 1 (1 – ) (1 – ) (1 – ) fm –
fm
bub
bub
model) phase fm
fm – –
Fluidized All phases r – – –
u i
beds
(L-K
model)
For all – – – – – M
Reactors S p
V S
a is the f ed-bed porosity (v ix oidage), is the bulk density of solids, is the particle density , m is the mass of
b p s
solid per unit volume of bubble-free liquid in slurry reactors, h and h are the fractional solid and liquid hold-
S L
up in slurry reactors, is the volume of a specific phase per unit volume of the fluid bubbles phase in fluidized
i
beds, and are the fraction of the bed occupied by fluid bubbles and the bed voidage at minimum flu-
bub fm
idization state in fluidized beds, respecti . ely v
b The reaction rate that is most commonly used in the analysis of the corresponding reactor type or model.
c Three- (slurry) and two-phase systems.
Another critical issue that definitely needs to be clarified is the surface of the catalyst
per unit volume of reactor or fluid, which is used in reactor analysis. ace area The total surf
of a catalyst includes the internal and the external surface areas. Thus
For fixed-beds:
• for porous particles,
S SM s s
S b (3.20)
s
V R V R
• for nonporous particles,
S ex (3.21)
V u
R