Page 74 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 74
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:44 PM Page 70
70 3. Heterogeneous Processes and Reactor Analysis
gas-liquid
interface
C G,i
C L,i
C S
C G
bulk gas
C L
solid
bulk liquid
g as film liquid film liquid film
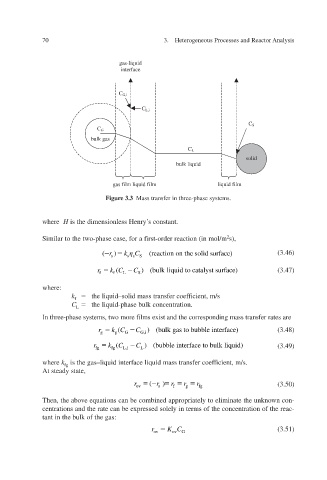
Figure 3.3 Mass transfer in three-phase systems.
where H is the dimensionless Henry’ s constant.
Similar to the two-phase case, for a first-order reaction (in mol/m 2 s),
( r ) C (reaction on the solid su rface) (3.46)
k
s s s S
r k C ( C ) (bk liqd to catt su s y al rface) (3.47)
l
u
i
u
f f L S
where:
k the liquid–solid mass transfer coef m/s icient, f
f
C the liquid-phase bulk concentration.
L
In three-phase systems, tw ilms e o more fxist and the corresponding mass transfer rates are
r k C ( C ) (bulk g to bubble i nt erface) (3.48)
as
g g G G,i
rfa
c
e
r k C ( C ) (bubble inte to bulk liquid) (3.49)
fg fg L,i L
where k fg is the gas–liquid interface liquid mass transfer coef m/s. icient, f
At steady state,
r
r ov r ( s r ) r (3.50)
g
fg
f
Then, the aboe equations can be combined appropriately to eliminate the unknown con- v
centrations and the rate can be expressed solely in terms of the concentration of the reac-
tant in the bulk of the gas:
r ov K C ov G (3.51)