Page 159 - Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of Structures
P. 159
Example of an RC Building Retrofitted by RC Shear Walls Chapter 3 151
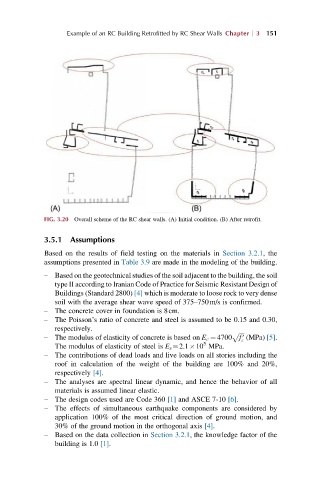
FIG. 3.20 Overall scheme of the RC shear walls. (A) Initial condition. (B) After retrofit.
3.5.1 Assumptions
Based on the results of field testing on the materials in Section 3.2.1, the
assumptions presented in Table 3.9 are made in the modeling of the building.
– Based on the geotechnical studies of the soil adjacent to the building, the soil
type II according to Iranian Code of Practice for Seismic Resistant Design of
Buildings (Standard 2800) [4] which is moderate to loose rock to very dense
soil with the average shear wave speed of 375–750m/s is confirmed.
– The concrete cover in foundation is 8cm.
– The Poisson’s ratio of concrete and steel is assumed to be 0.15 and 0.30,
respectively.
p ffiffiffiffi
– The modulus of elasticity of concrete is based on E c ¼ 4700 f (MPa) [5].
0
c
5
The modulus of elasticity of steel is E s ¼2.1 10 MPa.
– The contributions of dead loads and live loads on all stories including the
roof in calculation of the weight of the building are 100% and 20%,
respectively [4].
– The analyses are spectral linear dynamic, and hence the behavior of all
materials is assumed linear elastic.
– The design codes used are Code 360 [1] and ASCE 7-10 [6].
– The effects of simultaneous earthquake components are considered by
application 100% of the most critical direction of ground motion, and
30% of the ground motion in the orthogonal axis [4].
– Based on the data collection in Section 3.2.1, the knowledge factor of the
building is 1.0 [1].