Page 106 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 106
Chapter 5. Full calculations of plant eflciency 19
0.35
F
0
2 0.3
+
v)
3
2 095
G
U
0.2
0
b
0.15
E
9 0.1
U
i 0.05
0
0
0
0
1000 1200 1400 1600 I800 ZOO0 2200
COMBUSTION TEMPERATURE OC
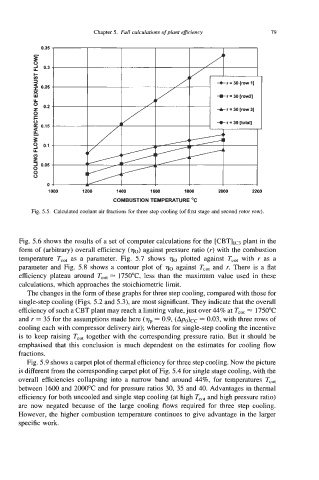
Fig. 5.5. Calculated coolant air fractions for three step cooling (of first stage and second rotor row)
Fig. 5.6 shows the results of a set of computer calculations for the [CBTIIC3 plant in the
form of (arbitrary) overall efficiency (70) against pressure ratio (r) with the combustion
temperature T,, as a parameter. Fig. 5.7 shows vo plotted against Tco, with r as a
parameter and Fig. 5.8 shows a contour plot of 70 against T,,, and r. There is a flat
efficiency plateau around T,,, = 175OoC, less than the maximum value used in these
calculations, which approaches the stoichiometric limit.
The changes in the form of these graphs for three step cooling, compared with those for
single-step cooling (Figs. 5.2 and 5.3), are most significant. They indicate that the overall
efficiency of such a CBT plant may reach a limiting value, just over 44% at T,, = 1750°C
and r = 35 for the assumptions made here (qp = 0.9, (Ap,-,)cc = 0.03, with three rows of
cooling each with compressor delivery air); whereas for single-step cooling the incentive
is to keep raising T,,, together with the corresponding pressure ratio. But it should be
emphasised that this conclusion is much dependent on the estimates for cooling flow
fractions.
Fig. 5.9 shows a carpet plot of thermal efficiency for three step cooling. Now the picture
is different from the corresponding carpet plot of Fig. 5.4 for single stage cooling, with the
overall efficiencies collapsing into a narrow band around 44%, for temperatures T,,,
between 1600 and 2000°C and for pressure ratios 30, 35 and 40. Advantages in thermal
efficiency for both uncooled and single step cooling (at high T,,, and high pressure ratio)
are now negated because of the large cooling flows required for three step cooling.
However, the higher combustion temperature continues to give advantage in the larger
specific work.