Page 230 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 230
192 Advanced gas turbine cycles
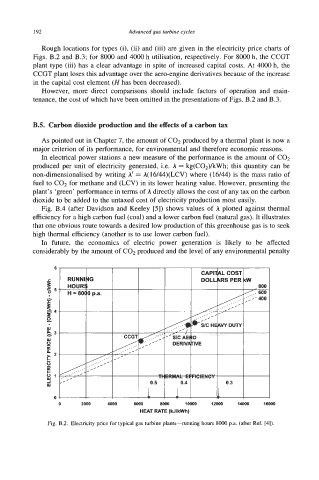
Rough locations for types (i), (ii) and (iii) are given in the electricity price charts of
Figs. B.2 and B.3; for 8000 and 4ooo h utilisation, respectively. For 8000 h, the CCGT
plant type (iii) has a clear advantage in spite of increased capital costs. At 4OOO h, the
CCGT plant loses this advantage over the aero-engine derivatives because of the increase
in the capital cost element (H has been decreased).
However, more direct comparisons should include factors of operation and main-
tenance, the cost of which have been omitted in the presentations of Figs. B.2 and B.3.
B.5. Carbon dioxide production and the effects of a carbon tax
As pointed out in Chapter 7, the amount of C02 produced by a thermal plant is now a
major criterion of its performance, for environmental and therefore economic reasons.
In electrical power stations a new measure of the performance is the amount of C02
produced per unit of electricity generated, i.e. A = kg(C0,)kWh; this quantity can be
non-dimensionalised by writing A’ = A( 16/44)(LCV) where (16/4) is the mass ratio of
fuel to C02 for methane and (LCV) in its lower heating value. However, presenting the
plant’s ‘green’ performance in terms of A directly allows the cost of any tax on the carbon
dioxide to be added to the untaxed cost of electricity production most easily.
Fig. B.4 (after Davidson and Keeley [5]) shows values of A plotted against thermal
efficiency for a high carbon fuel (coal) and a lower carbon fuel (natural gas). It illustrates
that one obvious route towards a desired low production of this greenhouse gas is to seek
high thermal efficiency (another is to use lower carbon fuel).
In future, the economics of electric power generation is likely to be affected
considerably by the amount of C02 produced and the level of any environmental penalty
8
0
0 2MH) 4000 Boo0 8OOo lo000 12OOo 14000 18ooo
HEAT RATE (kJ/kWh)
Fig. B.2. Electricity price for typical gas turbine plants-running hours 8000 p.a. (after Ref. [41).