Page 1041 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1041
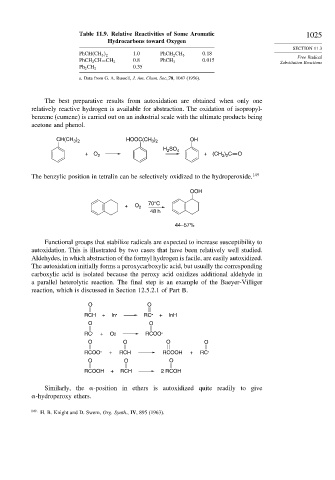
Table 11.9. Relative Reactivities of Some Aromatic 1025
Hydrocarbons toward Oxygen
SECTION 11.3
1 0 0 18
PhCH CH 3
2 PhCH 2 CH 3
Free Radical
0 8 0 015
PhCH 2 CH=CH 2 PhCH 3
Substitution Reactions
0 35
Ph 2 CH 2
a. Data from G. A. Russell, J. Am. Chem. Soc.,78, 1047 (1956).
The best preparative results from autoxidation are obtained when only one
relatively reactive hydrogen is available for abstraction. The oxidation of isopropyl-
benzene (cumene) is carried out on an industrial scale with the ultimate products being
acetone and phenol.
CH(CH ) HOOC(CH ) OH
3 2
3 2
H SO 4
2
+ O 2 + (CH ) C O
3 2
The benzylic position in tetralin can be selectively oxidized to the hydroperoxide. 149
OOH
+ O 2 70°C
48 h
44–57%
Functional groups that stabilize radicals are expected to increase susceptibility to
autoxidation. This is illustrated by two cases that have been relatively well studied.
Aldehydes, in which abstraction of the formyl hydrogen is facile, are easily autoxidized.
The autoxidation initially forms a peroxycarboxylic acid, but usually the corresponding
carboxylic acid is isolated because the peroxy acid oxidizes additional aldehyde in
a parallel heterolytic reaction. The final step is an example of the Baeyer-Villiger
reaction, which is discussed in Section 12.5.2.1 of Part B.
O O
RCH + In . RC . + InH
O O
RC . + O2 RCOO .
O O O O
. .
RCOO + RCH RCOOH + RC
O O O
RCOOH + RCH 2 RCOH
Similarly, the -position in ethers is autoxidized quite readily to give
-hydroperoxy ethers.
149
H. B. Knight and D. Swern, Org. Synth., IV, 895 (1963).