Page 31 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 31
deprotonation. The nature of the solvent determines the degree of ion pairing and 3
aggregation, which in turn affect reactivity.
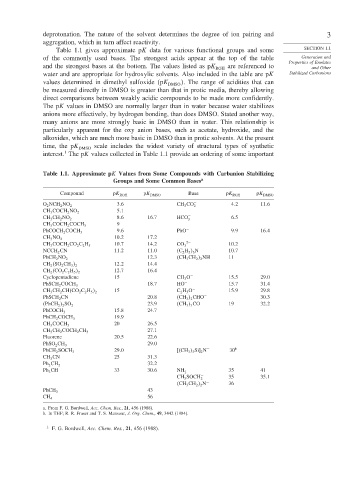
Table 1.1 gives approximate pK data for various functional groups and some SECTION 1.1
of the commonly used bases. The strongest acids appear at the top of the table Generation and
Properties of Enolates
and the strongest bases at the bottom. The values listed as pK are referenced to
ROH and Other
water and are appropriate for hydroxylic solvents. Also included in the table are pK Stabilized Carbanions
values determined in dimethyl sulfoxide pK DMSO . The range of acidities that can
be measured directly in DMSO is greater than that in protic media, thereby allowing
direct comparisons between weakly acidic compounds to be made more confidently.
The pK values in DMSO are normally larger than in water because water stabilizes
anions more effectively, by hydrogen bonding, than does DMSO. Stated another way,
many anions are more strongly basic in DMSO than in water. This relationship is
particularly apparent for the oxy anion bases, such as acetate, hydroxide, and the
alkoxides, which are much more basic in DMSO than in protic solvents. At the present
time, the pK DMSO scale includes the widest variety of structural types of synthetic
1
interest. The pK values collected in Table 1.1 provide an ordering of some important
Table 1.1. Approximate pK Values from Some Compounds with Carbanion Stabilizing
Groups and Some Common Bases a
Compound pK ROH pK DMSO Base pK ROH pK DMSO
3 6 CH 3 CO − 4 2 11 6
O 2 NCH 2 NO 2 2
5 1
CH 3 COCH 2 NO 2
8 6 16 7 HCO − 6 5
3
CH 3 CH 2 NO 2
9
CH 3 COCH 2 COCH 3
9 6 PhO − 9 9 16 4
PhCOCH 2 COCH 3
10 2 17 2
CH 3 NO 2
10 7 14 2 CO 2− 10 2
CH 3 COCH 2 CO 2 C 2 H 5
3
NCCH 2 CN 11 2 11 0 C 2 H 5 3 N 10 7
12 3 CH 3 CH 2 2 NH 11
PhCH 2 NO 2
12 2 14 4
CH 2 SO 2 CH 3 2
12 7 16 4
CH 2 CO 2 C 2 H 5 2
Cyclopentadiene 15 CH 3 O − 15 5 29 0
18 7 HO − 15 7 31 4
PhSCH 2 COCH 3
15 C 2 H 5 O − 15 9 29 8
CH 3 CH 2 CH CO 2 C 2 H 5 2
PhSCH 2 CN 20 8 CH 3 2 CHO − 30 3
23 9 CH 3 3 CO − 19 32 2
PhCH 2 2 SO 2
15 8 24 7
PhCOCH 3
19 9
PhCH 2 COCH 3
20 26 5
CH 3 COCH 3
27 1
CH 3 CH 2 COCH 2 CH 3
Fluorene 20 5 22 6
29 0
PhSO 2 CH 3
29 0 CH 3 3 Si 2 N − 30 b
PhCH 2 SOCH 3
CH 3 CN 25 31 3
32 2
Ph 2 CH 2
Ph 3 CH 33 30 6 NH − 2 35 41
CH 3 SOCH − 35 35 1
2
CH 3 CH 2 2 N − 36
43
PhCH 3
56
CH 4
a. From F. G. Bordwell, Acc. Chem. Res., 21, 456 (1988).
b. In THF; R. R. Fraser and T. S. Mansour, J. Org. Chem., 49, 3442 (1984).
1
F. G. Bordwell, Acc. Chem. Res., 21, 456 (1988).