Page 679 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 679
654 The catalytic cycle for these reactions is believed to involve dinuclear complexes
formed among the zinc chelate, the aldehyde, and the zinc atom that releases the
CHAPTER 7 nucleophile.
Organometallic
Compounds of Group I RZn OCHPh
and II Metals
R – +
N R Zn O CHPh
2
Zn R
O
N R
N R Zn
Zn O O CHPh
O O CHPh Zn
Zn R R R
R
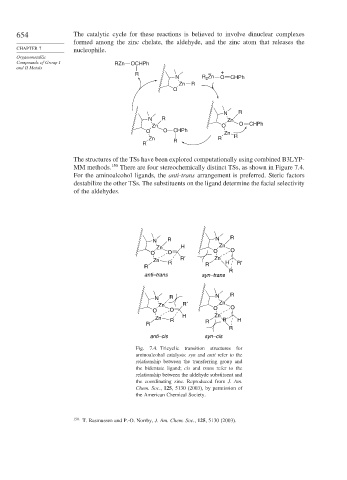
The structures of the TSs have been explored computationally using combined B3LYP-
MM methods. 150 There are four stereochemically distinct TSs, as shown in Figure 7.4.
For the aminoalcohol ligands, the anti-trans arrangement is preferred. Steric factors
destabilize the other TSs. The substituents on the ligand determine the facial selectivity
of the aldehydes.
N R N R
Zn H Zn
O O O O
Zn R R′ Zn H R′
R R
R
anti–trans syn–trans
N R N R
Zn R′ Zn O
O O O
Zn R H Zn R′ H
R R
R
anti–cis syn–cis
Fig. 7.4. Tricyclic transition structures for
aminoalcohol catalysts: syn and anti refer to the
relationship between the transferring group and
the bidentate ligand; cis and trans refer to the
relationship between the aldehyde substituent and
the coordinating zinc. Reproduced from J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 125, 5130 (2003), by permission of
the American Chemical Society.
150
T. Rasmussen and P.-O. Norrby, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 5130 (2003).