Page 984 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 984
960 radicals are ethene derivatives with electron-attracting groups, such as cyano, ester,
or other carbonyl substituents. 302 There are three factors that make such compounds
CHAPTER 10 particularly useful: (1) alkyl radicals are relatively nucleophilic and react at enhanced
Reactions Involving rates with alkenes having EWG substituents; (2) alkenes with such substituents exhibit
Carbocations, Carbenes,
and Radicals as Reactive a good degree of regioselectivity, resulting from a combination of steric and radical-
Intermediates stabilizing effects of the substituent; (3) the EWG substituent makes the adduct radical
more electrophilic and increases the rate of the subsequent hydrogen abstraction step.
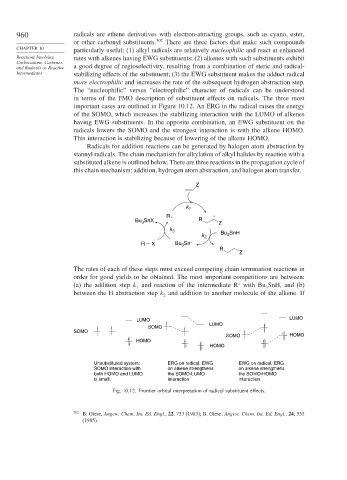
The “nucleophilic” versus “electrophilic” character of radicals can be understood
in terms of the FMO description of substituent effects on radicals. The three most
important cases are outlined in Figure 10.12. An ERG in the radical raises the energy
of the SOMO, which increases the stabilizing interaction with the LUMO of alkenes
having EWG substituents. In the opposite combination, an EWG substituent on the
radicals lowers the SOMO and the strongest interaction is with the alkene HOMO.
This interaction is stabilizing because of lowering of the alkene HOMO.
Radicals for addition reactions can be generated by halogen atom abstraction by
stannyl radicals. The chain mechanism for alkylation of alkyl halides by reaction with a
substituted alkene is outlined below. There are three reactions in the propagation cycle of
this chain mechanism: addition, hydrogen atom abstraction, and halogen atom transfer.
Z
k 1
R . .
SnX R
Bu 3
Z
k 3
3
k 2 Bu SnH
R X Bu Sn .
3
R
Z
The rates of each of these steps must exceed competing chain termination reactions in
order for good yields to be obtained. The most important competitions are between:
.
(a) the addition step k and reaction of the intermediate R with Bu SnH, and (b)
3
1
between the H abstraction step k and addition to another molecule of the alkene. If
2
LUMO
LUMO
LUMO
SOMO
SOMO
SOMO HOMO
HOMO
HOMO
Unsubstituted system: ERG on radical; EWG EWG on radical, ERG
SOMO interaction with on alkene strengthens on alkene strengthens
both HOMO and LUMO the SOMO-LUMO the SOMO-HOMO
is small. interaction interaction
Fig. 10.12. Frontier orbital interpretation of radical substituent effects.
302
B. Giese, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 22, 753 (1983); B. Giese, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 24, 553
(1985).