Page 125 - Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, Second Edition
P. 125
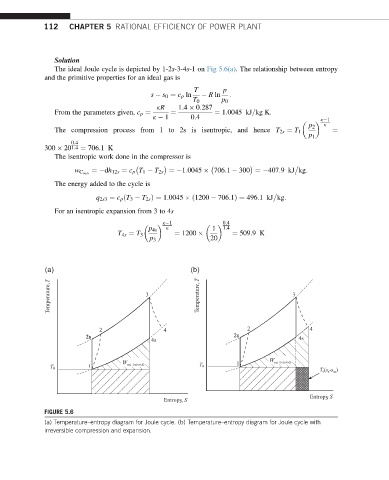
112 CHAPTER 5 RATIONAL EFFICIENCY OF POWER PLANT
Solution
The ideal Joule cycle is depicted by 1-2s-3-4s-1 on Fig 5.6(a). The relationship between entropy
and the primitive properties for an ideal gas is
T p
s s 0 ¼ c p ln R ln :
T 0 p 0
kR 1:4 0:287
¼ 1:0045 kJ=kg K:
From the parameters given, c p ¼ ¼
k 1 0:4
k 1
k
p 2
The compression process from 1 to 2s is isentropic, and hence T 2s ¼ T 1 ¼
p 1
0:4
300 201:4 ¼ 706:1K
The isentropic work done in the compressor is
¼ dh 12s ¼ c p T 1 T 2s ¼ 1:0045 706:1 300 ¼ 407:9kJ kg:
w C isen
The energy added to the cycle is
q 2s3 ¼ c p ðT 3 T 2s Þ¼ 1:0045 ð1200 706:1Þ¼ 496:1kJ kg:
For an isentropic expansion from 3 to 4s
k 1 0:4
k 1 1:4
p 4s
T 4s ¼ T 3 ¼ 1200 ¼ 509:9K
p 3 20
(a) (b)
Temperature, T 3 Temperature, T 3
2 4 2 4
2 2ss 2s 2s 4s
4s
1 W net (rejected) T 0 1 1 W net (rejected)
T 0
T (s -s )
0
4
4s
Entropy, S
Entropy, S
FIGURE 5.6
(a) Temperature–entropy diagram for Joule cycle. (b) Temperature–entropy diagram for Joule cycle with
irreversible compression and expansion.