Page 131 - Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, Second Edition
P. 131
118 CHAPTER 5 RATIONAL EFFICIENCY OF POWER PLANT
P5.5 A steam turbine operates on a superheated Rankine cycle. The pressure and temperature of the
steam leaving the boiler are 10 bar and 350 C respectively. The specific steam consumption
of the plant is 4.55 kg/kWh. The pressure in the condenser is 0.05 bar.
If the feed pump work may be neglected, calculate the thermal efficiency of the plant, the
turbine isentropic efficiency and evaluate the rational efficiency. Also calculate the mean
temperature of reception of heat in the boiler and use this in conjunction with the condenser
temperature to evaluate the thermal efficiency. Explain why the value calculated by this method
is higher than that obtained previously.
[26.5%; 86%; 84.84%; 30.85%]
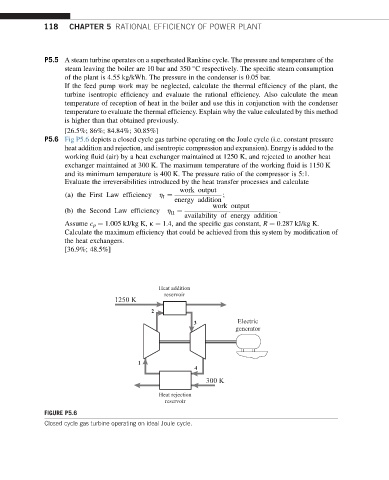
P5.6 Fig P5.6 depicts a closed cycle gas turbine operating on the Joule cycle (i.e. constant pressure
heat addition and rejection, and isentropic compression and expansion). Energy is added to the
working fluid (air) by a heat exchanger maintained at 1250 K, and rejected to another heat
exchanger maintained at 300 K. The maximum temperature of the working fluid is 1150 K
and its minimum temperature is 400 K. The pressure ratio of the compressor is 5:1.
Evaluate the irreversibilities introduced by the heat transfer processes and calculate
work output
(a) the First Law efficiency h ¼ ;
I
energy addition
work output
(b) the Second Law efficiency h ¼ :
II
availability of energy addition
Assume c p ¼ 1.005 kJ/kg K, k ¼ 1.4, and the specific gas constant, R ¼ 0.287 kJ/kg K.
Calculate the maximum efficiency that could be achieved from this system by modification of
the heat exchangers.
[36.9%; 48.5%]
Heat addition
reservoir
1250 K
2
3 Electric
generator
1
4
300 K
Heat rejection
reservoir
FIGURE P5.6
Closed cycle gas turbine operating on ideal Joule cycle.