Page 248 - Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, Second Edition
P. 248
236 CHAPTER 11 CHEMISTRY OF COMBUSTION
Gaseous
atoms
ΣΔ H ΣΔ H(X-Y)
ΣΔ H(X-Y)
Elemental
molecules
Δ
( H )
Δ
( H )
Reactant
molecules
Δ H =
(Δ H ) − (Δ H )
Product
molecules
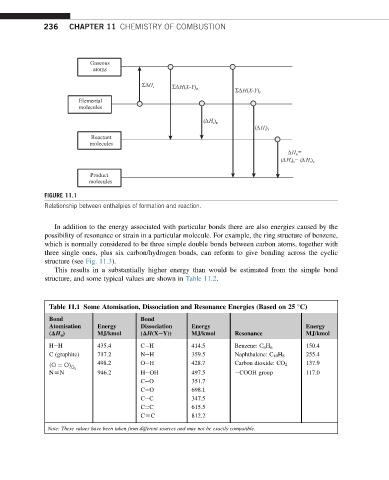
FIGURE 11.1
Relationship between enthalpies of formation and reaction.
In addition to the energy associated with particular bonds there are also energies caused by the
possibility of resonance or strain in a particular molecule. For example, the ring structure of benzene,
which is normally considered to be three simple double bonds between carbon atoms, together with
three single ones, plus six carbon/hydrogen bonds, can reform to give bonding across the cyclic
structure (see Fig. 11.3).
This results in a substantially higher energy than would be estimated from the simple bond
structure, and some typical values are shown in Table 11.2.
Table 11.1 Some Atomisation, Dissociation and Resonance Energies (Based on 25 C)
Bond Bond
Atomisation Energy Dissociation Energy Energy
(DH a ) MJ/kmol (DH(XeY)) MJ/kmol Resonance MJ/kmol
HeH 435.4 C H 414.5 Benzene: C 6 H 6 150.4
C (graphite) 717.2 NeH 359.5 Naphthalene: C 10 H 8 255.4
498.2 OeH 428.7 Carbon dioxide: CO 2 137.9
ðO ¼ OÞ
O 2
NhN 946.2 HeOH 497.5 COOH group 117.0
CeO 351.7
C¼O 698.1
CeC 347.5
C¼C 615.5
ChC 812.2
Note: These values have been taken from different sources and may not be exactly compatible.