Page 228 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 228
10.4 APPLICATION OF THE ENERGY EQUATION 215
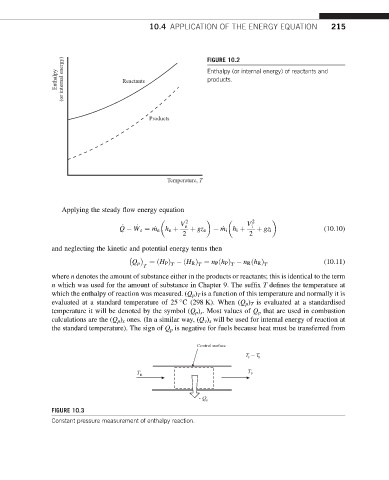
Enthalpy (or internal energy) of reactants and
Enthalpy (or internal energy) Reactants FIGURE 10.2
products.
Products
Temperature, T
Applying the steady flow energy equation
2 2
_ _ V e V i
Q W s ¼ _ m e h e þ þ gz e _ m i h i þ þ gz i (10.10)
2 2
and neglecting the kinetic and potential energy terms then
Q p ¼ðH P Þ ðH R Þ ¼ n P ðh P Þ n R ðh R Þ (10.11)
T T T T T
where n denotes the amount of substance either in the products or reactants; this is identical to the term
n which was used for the amount of substance in Chapter 9. The suffix T defines the temperature at
which the enthalpy of reaction was measured. (Q p ) T is a function of this temperature and normally it is
evaluated at a standard temperature of 25 C (298 K). When (Q p ) T is evaluated at a standardised
temperature it will be denoted by the symbol (Q p ) s . Most values of Q p that are used in combustion
calculations are the (Q p ) s ones. (In a similar way, (Q v ) s will be used for internal energy of reaction at
the standard temperature). The sign of Q p is negative for fuels because heat must be transferred from
Control surface
T = T R
P
T P
T R
- Q p
FIGURE 10.3
Constant pressure measurement of enthalpy reaction.