Page 235 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 235
222 CHAPTER 10 THERMODYNAMICS OF COMBUSTION
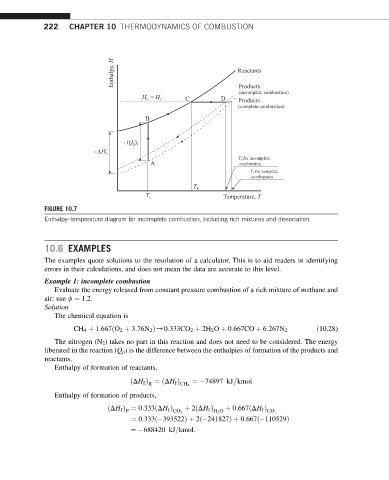
Enthalpy, H Reactants
Products
(incomplete combustion)
H = H P C D Products
R
(complete combustion)
B
- (Q )
ps
- H 0
T for incomplete
A combustion
T for complete
combustion
T R
T s Temperature, T
FIGURE 10.7
Enthalpy–temperature diagram for incomplete combustion, including rich mixtures and dissociation.
10.6 EXAMPLES
The examples quote solutions to the resolution of a calculator. This is to aid readers in identifying
errors in their calculations, and does not mean the data are accurate to this level.
Example 1: incomplete combustion
Evaluate the energy released from constant pressure combustion of a rich mixture of methane and
air: use f ¼ 1.2.
Solution
The chemical equation is
CH 4 þ 1:667ðO 2 þ 3:76N 2 Þ/0:333CO 2 þ 2H 2 O þ 0:667CO þ 6:267N 2 (10.28)
The nitrogen (N 2 ) takes no part in this reaction and does not need to be considered. The energy
liberated in the reaction (Q p ) is the difference between the enthalpies of formation of the products and
reactants.
Enthalpy of formation of reactants,
ðDH f Þ ¼ðDH f Þ CH 4 ¼ 74897 kJ kmol
R
Enthalpy of formation of products,
ðDH f Þ ¼ 0:333ðDH f Þ CO 2 þ 2ðDH f Þ H 2 O þ 0:667ðDH f Þ CO
P
¼ 0:333ð 393522Þþ 2ð 241827Þþ 0:667ð 110529Þ
¼ 688420 kJ=kmol: