Page 238 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 238
10.6 EXAMPLES 225
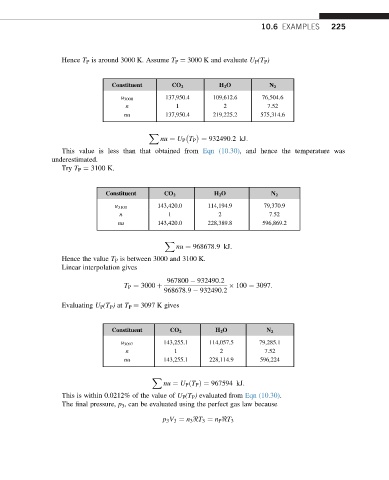
Hence T P is around 3000 K. Assume T P ¼ 3000 K and evaluate U P (T P )
Constituent CO 2 H 2 O N 2
137,950.4 109,612.6 76,504.6
u 3000
n 1 2 7.52
nu 137,950.4 219,225.2 575,314.6
X
nu ¼ U P T P ¼ 932490:2kJ:
This value is less than that obtained from Eqn (10.30), and hence the temperature was
underestimated.
Try T P ¼ 3100 K.
Constituent CO 2 H 2 O N 2
143,420.0 114,194.9 79,370.9
u 3100
n 1 2 7.52
nu 143,420.0 228,389.8 596,869.2
X
nu ¼ 968678:9kJ:
Hence the value T P is between 3000 and 3100 K.
Linear interpolation gives
967800 932490:2
T P ¼ 3000 þ 100 ¼ 3097:
968678:9 932490:2
Evaluating U P (T P ) at T P ¼ 3097 K gives
Constituent CO 2 H 2 O N 2
143,255.1 114,057.5 79,285.1
u 3097
n 1 2 7.52
nu 143,255.1 228,114.9 596,224
X
nu ¼ U P ðT P Þ¼ 967594 kJ:
This is within 0.0212% of the value of U P (T P ) evaluated from Eqn (10.30).
The final pressure, p 3 , can be evaluated using the perfect gas law because
p 3 V 3 ¼ n 3 <T 3 ¼ n P <T 3