Page 383 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 383
372 CHAPTER 16 RECIPROCATING INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
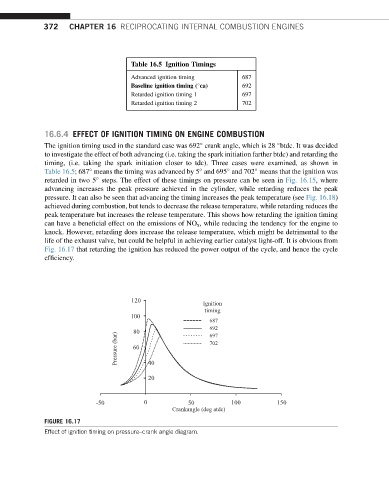
Table 16.5 Ignition Timings
Advanced ignition timing 687
Baseline ignition timing ( ca) 692
Retarded ignition timing 1 697
Retarded ignition timing 2 702
16.6.4 EFFECT OF IGNITION TIMING ON ENGINE COMBUSTION
The ignition timing used in the standard case was 692 crank angle, which is 28 btdc. It was decided
to investigate the effect of both advancing (i.e. taking the spark initiation farther btdc) and retarding the
timing, (i.e. taking the spark initiation closer to tdc). Three cases were examined, as shown in
Table 16.5; 687 means the timing was advanced by 5 and 695 and 702 means that the ignition was
retarded in two 5 steps. The effect of these timings on pressure can be seen in Fig. 16.15, where
advancing increases the peak pressure achieved in the cylinder, while retarding reduces the peak
pressure. It can also be seen that advancing the timing increases the peak temperature (see Fig. 16.18)
achieved during combustion, but tends to decrease the release temperature, while retarding reduces the
peak temperature but increases the release temperature. This shows how retarding the ignition timing
can have a beneficial effect on the emissions of NO x , while reducing the tendency for the engine to
knock. However, retarding does increase the release temperature, which might be detrimental to the
life of the exhaust valve, but could be helpful in achieving earlier catalyst light-off. It is obvious from
Fig. 16.17 that retarding the ignition has reduced the power output of the cycle, and hence the cycle
efficiency.
120
Ignition
timing
100
687
692
80 697
Pressure (bar) 60 40 702
20
-50 0 50 100 150
Crankangle (deg atdc)
FIGURE 16.17
Effect of ignition timing on pressure–crank angle diagram.