Page 134 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 134
Characteristics of Respirable Coal Dust Particles 115
Taking the log to the base, we have:
ln lnð1=1 yÞ¼ nlnx nlnk (8.26)
Hence a plot of ln ln 1 against ln x yields a straight line. The gradient of the
1 y
straight line is the constant, n, that is a characteristic of the broken material. The RR
graph paper enables direct plotting of the cumulative mass fraction undersize, y against
particle size, x. On this graph, k is the characteristic size parameter corresponding to
63.21% undersize. This is easily derived by putting x ¼ k, in Eq. (8.25). Typical
values of n and k for some coal types are shown in Table 8.4 for 37 mm particles [1].
A smaller value of n means a flatter gradient of mass distribution and hence a higher
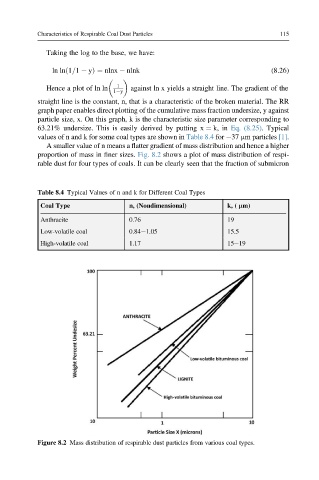
proportion of mass in finer sizes. Fig. 8.2 shows a plot of mass distribution of respi-
rable dust for four types of coals. It can be clearly seen that the fraction of submicron
Table 8.4 Typical Values of n and k for Different Coal Types
Coal Type n, (Nondimensional) k, ( mm)
Anthracite 0.76 19
Low-volatile coal 0.84e1.05 15.5
High-volatile coal 1.17 15e19
Figure 8.2 Mass distribution of respirable dust particles from various coal types.