Page 172 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 172
152 Advanced Mine Ventilation
Figure 10.7 The dust suppression test facility.
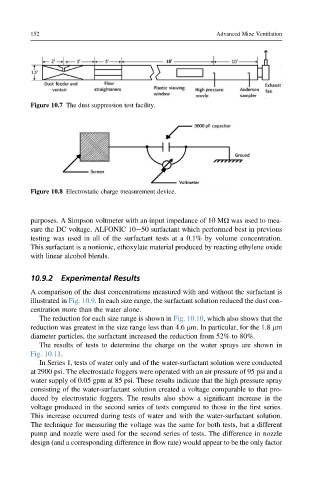
Figure 10.8 Electrostatic charge measurement device.
purposes. A Simpson voltmeter with an input impedance of 10 MU was used to mea-
sure the DC voltage. ALFONIC 10e50 surfactant which performed best in previous
testing was used in all of the surfactant tests at a 0.1% by volume concentration.
This surfactant is a nonionic, ethoxylate material produced by reacting ethylene oxide
with linear alcohol blends.
10.9.2 Experimental Results
A comparison of the dust concentrations measured with and without the surfactant is
illustrated in Fig. 10.9. In each size range, the surfactant solution reduced the dust con-
centration more than the water alone.
The reduction for each size range is shown in Fig. 10.10, which also shows that the
reduction was greatest in the size range less than 4.6 mm. In particular, for the 1.8 mm
diameter particles, the surfactant increased the reduction from 52% to 80%.
The results of tests to determine the charge on the water sprays are shown in
Fig. 10.11.
In Series 1, tests of water only and of the water-surfactant solution were conducted
at 2900 psi. The electrostatic foggers were operated with an air pressure of 95 psi and a
water supply of 0.05 gpm at 85 psi. These results indicate that the high pressure spray
consisting of the water-surfactant solution created a voltage comparable to that pro-
duced by electrostatic foggers. The results also show a significant increase in the
voltage produced in the second series of tests compared to those in the first series.
This increase occurred during tests of water and with the water-surfactant solution.
The technique for measuring the voltage was the same for both tests, but a different
pump and nozzle were used for the second series of tests. The difference in nozzle
design (and a corresponding difference in flow rate) would appear to be the only factor