Page 314 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 314
Floor Gas Emissions and Gas Outbursts 291
17.3.1 Australia
Gas outburst risk is assessed by
3
3
1. Gas contents (limit 212 ft /ton for CO 2 ; 318 ft /ton for CH 4 ).
2. Gas type (CH 4 or CO 2 ).
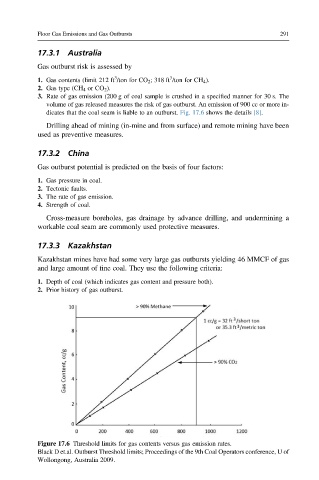
3. Rate of gas emission (200 g of coal sample is crushed in a specified manner for 30 s. The
volume of gas released measures the risk of gas outburst. An emission of 900 cc or more in-
dicates that the coal seam is liable to an outburst. Fig. 17.6 shows the details [8].
Drilling ahead of mining (in-mine and from surface) and remote mining have been
used as preventive measures.
17.3.2 China
Gas outburst potential is predicted on the basis of four factors:
1. Gas pressure in coal.
2. Tectonic faults.
3. The rate of gas emission.
4. Strength of coal.
Cross-measure boreholes, gas drainage by advance drilling, and undermining a
workable coal seam are commonly used protective measures.
17.3.3 Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan mines have had some very large gas outbursts yielding 46 MMCF of gas
and large amount of fine coal. They use the following criteria:
1. Depth of coal (which indicates gas content and pressure both).
2. Prior history of gas outburst.
Figure 17.6 Threshold limits for gas contents versus gas emission rates.
Black D et.al. Outburst Threshold limits; Proceedings of the 9th Coal Operators conference, U of
Wollongong, Australia 2009.