Page 319 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 319
296 Advanced Mine Ventilation
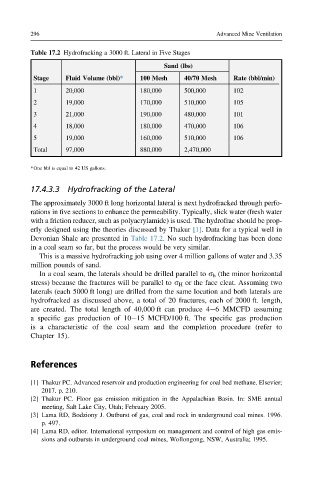
Table 17.2 Hydrofracking a 3000 ft. Lateral in Five Stages
Sand (lbs)
Stage Fluid Volume (bbl)* 100 Mesh 40/70 Mesh Rate (bbl/min)
1 20,000 180,000 500,000 102
2 19,000 170,000 510,000 105
3 21,000 190,000 480,000 101
4 18,000 180,000 470,000 106
5 19,000 160,000 510,000 106
Total 97,000 880,000 2,470,000
*One bbl is equal to 42 US gallons.
17.4.3.3 Hydrofracking of the Lateral
The approximately 3000 ft long horizontal lateral is next hydrofracked through perfo-
rations in five sections to enhance the permeability. Typically, slick water (fresh water
with a friction reducer, such as polyacrylamide) is used. The hydrofrac should be prop-
erly designed using the theories discussed by Thakur [1]. Data for a typical well in
Devonian Shale are presented in Table 17.2. No such hydrofracking has been done
in a coal seam so far, but the process would be very similar.
This is a massive hydrofracking job using over 4 million gallons of water and 3.35
million pounds of sand.
In a coal seam, the laterals should be drilled parallel to s h (the minor horizontal
stress) because the fractures will be parallel to s H or thefacecleat.Assuming two
laterals (each 5000 ft long) are drilled from the same location and both laterals are
hydrofracked as discussed above, a total of 20 fractures, each of 2000 ft. length,
are created. The total length of 40,000 ft can produce 4e6MMCFD assuming
a specific gas production of 10e15 MCFD/100 ft. The specific gas production
is a characteristic of the coal seam and the completion procedure (refer to
Chapter 15).
References
[1] Thakur PC. Advanced reservoir and production engineering for coal bed methane. Elsevier;
2017. p. 210.
[2] Thakur PC. Floor gas emission mitigation in the Appalachian Basin. In: SME annual
meeting, Salt Lake City, Utah; February 2005.
[3] Lama RD, Bodziony J. Outburst of gas, coal and rock in underground coal mines. 1996.
p. 497.
[4] Lama RD, editor. International symposium on management and control of high gas emis-
sions and outbursts in underground coal mines, Wollongong, NSW, Australia; 1995.