Page 384 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 384
Spontaneous Combustion of Coal 353
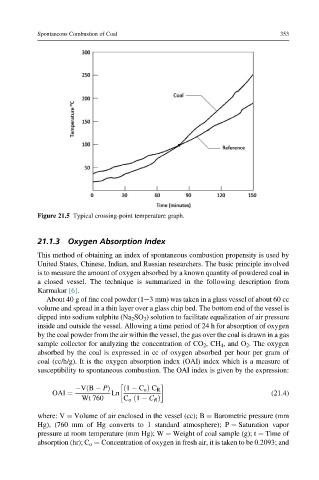
Figure 21.5 Typical crossing-point temperature graph.
21.1.3 Oxygen Absorption Index
This method of obtaining an index of spontaneous combustion propensity is used by
United States, Chinese, Indian, and Russian researchers. The basic principle involved
is to measure the amount of oxygen absorbed by a known quantity of powdered coal in
a closed vessel. The technique is summarized in the following description from
Karmakar [6].
About 40 g of fine coal powder (1e3 mm) was taken in a glass vessel of about 60 cc
volume and spread in a thin layer over a glass chip bed. The bottom end of the vessel is
dipped into sodium sulphite (Na 2 SO 3 ) solution to facilitate equalization of air pressure
inside and outside the vessel. Allowing a time period of 24 h for absorption of oxygen
by the coal powder from the air within the vessel, the gas over the coal is drawn in a gas
sample collector for analyzing the concentration of CO 2 ,CH 4 , and O 2 . The oxygen
absorbed by the coal is expressed in cc of oxygen absorbed per hour per gram of
coal (cc/h/g). It is the oxygen absorption index (OAI) index which is a measure of
susceptibility to spontaneous combustion. The OAI index is given by the expression:
VðB PÞ ð1 C o Þ C R
OAI ¼ Ln (21.4)
Wt 760 C o ð1 C R Þ
where: V ¼ Volume of air enclosed in the vessel (cc); B ¼ Barometric pressure (mm
Hg), (760 mm of Hg converts to 1 standard atmosphere); P ¼ Saturation vapor
pressure at room temperature (mm Hg); W ¼ Weight of coal sample (g); t ¼ Time of
absorption (hr); C o ¼ Concentration of oxygen in fresh air, it is taken to be 0.2093; and