Page 80 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 80
Ventilation Network Analysis 63
5.1 Network Analysis for Air Quantities and Pressure
All computer programs that analyze the air quantity and corresponding pressure loss
basically use Kirchoff’s first and second laws for transmission of electric power.
This is possible because pressure and quantity relation in mine ventilation
2
(P ¼ RQ ) is quite similar to electric current flow where:
2
V ¼ RI (5.1)
where: V is the voltage, R is the resistance, and I is the current.
5.1.1 Kirchoff’s First Law
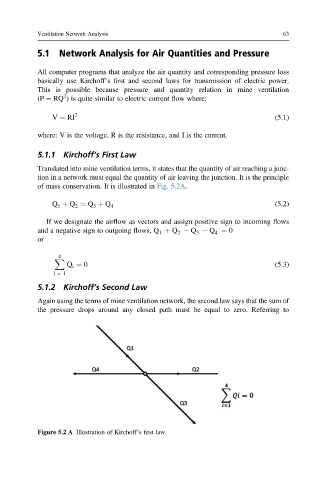
Translated into mine ventilation terms, it states that the quantity of air reaching a junc-
tion in a network must equal the quantity of air leaving the junction. It is the principle
of mass conservation. It is illustrated in Fig. 5.2A.
Q þ Q ¼ Q þ Q 4 (5.2)
2
1
3
If we designate the airflow as vectors and assign positive sign to incoming flows
and a negative sign to outgoing flows, Q þ Q Q Q ¼ 0
3
1
2
4
or
4
X
Q ¼ 0 (5.3)
i
i ¼ 1
5.1.2 Kirchoff’s Second Law
Again using the terms of mine ventilation network, the second law says that the sum of
the pressure drops around any closed path must be equal to zero. Referring to
Figure 5.2 A Illustration of Kirchoff’s first law.