Page 283 - Advances In Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
P. 283
Sustainable coal waste disposal practices 259
pH
0.8% 9
0.7% 8
Cumulative extraction 0.5% 6
0.6%
7
0.4%
5
0.3%
4
0.2%
2
0.1% 3
0.0% 1
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Leach cycle
FC-7 Cl FC-9 Cl FC-11 Cl
FC-8 Cl FC-10 Cl FC-12 Cl
CCPW pH CCPW/FCPW pH CCPW/FCPW/Ls pH
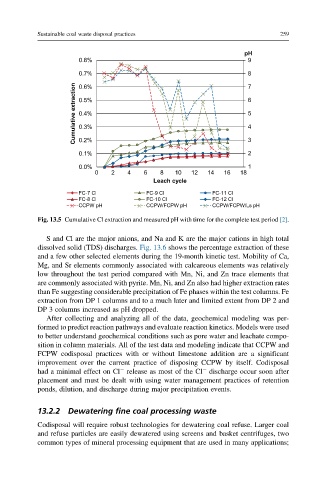
Fig. 13.5 Cumulative Cl extraction and measured pH with time for the complete test period [2].
S and Cl are the major anions, and Na and K are the major cations in high total
dissolved solid (TDS) discharges. Fig. 13.6 shows the percentage extraction of these
and a few other selected elements during the 19-month kinetic test. Mobility of Ca,
Mg, and Sr elements commonly associated with calcareous elements was relatively
low throughout the test period compared with Mn, Ni, and Zn trace elements that
are commonly associated with pyrite. Mn, Ni, and Zn also had higher extraction rates
than Fe suggesting considerable precipitation of Fe phases within the test columns. Fe
extraction from DP 1 columns and to a much later and limited extent from DP 2 and
DP 3 columns increased as pH dropped.
After collecting and analyzing all of the data, geochemical modeling was per-
formed to predict reaction pathways and evaluate reaction kinetics. Models were used
to better understand geochemical conditions such as pore water and leachate compo-
sition in column materials. All of the test data and modeling indicate that CCPW and
FCPW codisposal practices with or without limestone addition are a significant
improvement over the current practice of disposing CCPW by itself. Codisposal
had a minimal effect on Cl release as most of the Cl discharge occur soon after
placement and must be dealt with using water management practices of retention
ponds, dilution, and discharge during major precipitation events.
13.2.2 Dewatering fine coal processing waste
Codisposal will require robust technologies for dewatering coal refuse. Larger coal
and refuse particles are easily dewatered using screens and basket centrifuges, two
common types of mineral processing equipment that are used in many applications;