Page 62 - Advances in bioenergy (2016)
P. 62
−1
40
jecorina display k values of 2–20 sec on amorphous cellulose that corresponds to
cat
41
sixfold lower rates on crystalline cellulose. On the other hand, the efficiency of the protein
production has been improved approximately 10-fold, resulting in a serious decrease of the
cost of cellulases from approximately $0.20 to $0.50 per gallon of ethanol produced. 39
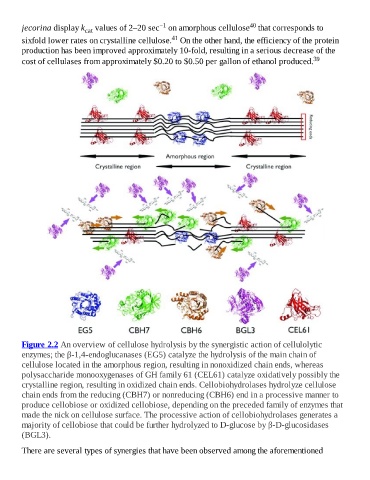
Figure 2.2 An overview of cellulose hydrolysis by the synergistic action of cellulolytic
enzymes; the β-1,4-endoglucanases (EG5) catalyze the hydrolysis of the main chain of
cellulose located in the amorphous region, resulting in nonoxidized chain ends, whereas
polysaccharide monooxygenases of GH family 61 (CEL61) catalyze oxidatively possibly the
crystalline region, resulting in oxidized chain ends. Cellobiohydrolases hydrolyze cellulose
chain ends from the reducing (CBH7) or nonreducing (CBH6) end in a processive manner to
produce cellobiose or oxidized cellobiose, depending on the preceded family of enzymes that
made the nick on cellulose surface. The processive action of cellobiohydrolases generates a
majority of cellobiose that could be further hydrolyzed to D-glucose by β-D-glucosidases
(BGL3).
There are several types of synergies that have been observed among the aforementioned