Page 108 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 108
Prospects of biodiesel feedstock as an effective ecofuel source and their challenges 81
evaluated the benefit of using ultrasonic preirradiation before extracting oil from
almond and apricot seeds by the aqueous enzymatic oil extraction process.
Abdulkarim et al. [66] reported the use of enzymes in commercial extraction of oil
from olives. The disadvantages of using enzymes are the high cost and long processing
time [22, 57].
3.3.4 Supercritical fluid method of extraction
The application of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), particularly the use of liquid
and supercritical carbon dioxide, has gained acceptance in recent years. This separa-
tion technique offers extraction yields comparable to those obtained by conventional
extraction methods using organic solvents [60]. This process produces highly purified
extracts that are free of potentially harmful solvent residues; extraction and separation
are quick as well as safe for thermally sensitive products. Also, the fractionation
of specific compounds is feasible, which may reduce separation costs as well as
possibly counteracting greenhouse gas effects by using CO 2 waste from industry
[20]. Moreover, in contrast with organic solvents, carbon dioxide is nontoxic, non-
flammable, noncorrosive, cheap, and readily available in large quantities with high
purity. Because CO 2 also has a relatively low critical pressure (73.8atm) and critical
temperature (31.1°C), it can be considered an ideal solvent for the treatment of natural
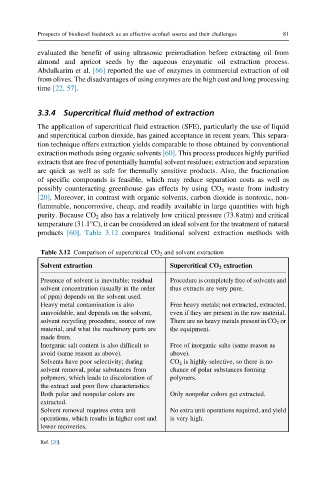
products [60]. Table 3.12 compares traditional solvent extraction methods with
Table 3.12 Comparison of supercritical CO 2 and solvent extraction
Solvent extraction Supercritical CO 2 extraction
Presence of solvent is inevitable; residual Procedure is completely free of solvents and
solvent concentration (usually in the order thus extracts are very pure.
of ppm) depends on the solvent used.
Heavy metal contamination is also Free heavy metals; not extracted, extracted,
unavoidable, and depends on the solvent, even if they are present in the raw material.
solvent recycling procedure, source of raw There are no heavy metals present in CO 2 or
material, and what the machinery parts are the equipment.
made from.
Inorganic salt content is also difficult to Free of inorganic salts (same reason as
avoid (same reason as above). above).
Solvents have poor selectivity; during CO 2 is highly selective, so there is no
solvent removal, polar substances from chance of polar substances forming
polymers, which leads to discoloration of polymers.
the extract and poor flow characteristics.
Both polar and nonpolar colors are Only nonpolar colors get extracted.
extracted.
Solvent removal requires extra unit No extra unit operations required, and yield
operations, which results in higher cost and is very high.
lower recoveries.
Ref. [20].