Page 236 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 236
200 Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
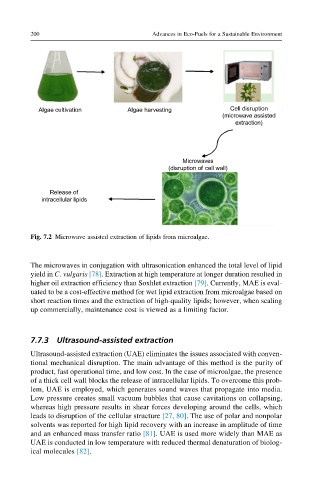
Algae cultivation Algae harvesting Cell disruption
(microwave assisted
extraction)
Microwaves
(disruption of cell wall)
Release of
intracellular lipids
Fig. 7.2 Microwave assisted extraction of lipids from microalgae.
The microwaves in conjugation with ultrasonication enhanced the total level of lipid
yield in C. vulgaris [78]. Extraction at high temperature at longer duration resulted in
higher oil extraction efficiency than Soxhlet extraction [79]. Currently, MAE is eval-
uated to be a cost-effective method for wet lipid extraction from microalgae based on
short reaction times and the extraction of high-quality lipids; however, when scaling
up commercially, maintenance cost is viewed as a limiting factor.
7.7.3 Ultrasound-assisted extraction
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) eliminates the issues associated with conven-
tional mechanical disruption. The main advantage of this method is the purity of
product, fast operational time, and low cost. In the case of microalgae, the presence
of a thick cell wall blocks the release of intracellular lipids. To overcome this prob-
lem, UAE is employed, which generates sound waves that propagate into media.
Low pressure creates small vacuum bubbles that cause cavitations on collapsing,
whereas high pressure results in shear forces developing around the cells, which
leads to disruption of the cellular structure [27, 80]. The use of polar and nonpolar
solvents was reported for high lipid recovery with an increase in amplitude of time
and an enhanced mass transfer ratio [81]. UAE is used more widely than MAE as
UAE is conducted in low temperature with reduced thermal denaturation of biolog-
ical molecules [82].