Page 42 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 42
Ecofuel feedstocks and their prospects 19
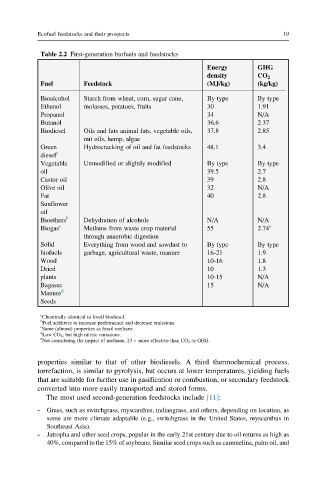
Table 2.2 First-generation biofuels and feedstocks
Energy GHG
density CO 2
Fuel Feedstock (MJ/kg) (kg/kg)
Bioalcohol Starch from wheat, corn, sugar cane, By type By type
Ethanol molasses, potatoes, fruits 30 1.91
Propanol 34 N/A
Butanol 36.6 2.37
Biodiesel Oils and fats animal fats, vegetable oils, 37.8 2.85
nut oils, hemp, algae
Green Hydrocracking of oil and fat feedstocks 48.1 3.4
diesel a
Vegetable Unmodified or slightly modified By type By type
oil 39.5 2.7
Castor oil 39 2.8
Olive oil 32 N/A
Fat 40 2.8
Sunflower
oil
Bioethers b Dehydration of alcohols N/A N/A
Biogas c Methane from waste crop material 55 2.74 e
through anaerobic digestion
Solid Everything from wood and sawdust to By type By type
biofuels garbage, agricultural waste, manure 16-21 1.9
Wood 10-16 1.8
Dried 10 1.3
plants 10-15 N/A
Bagasse 15 N/A
Manure d
Seeds
a
Chemically identical to fossil biodiesel.
b
Fuel additives to increase performance and decrease emissions.
c
Same (almost) properties as fossil methane.
d
Low CO 2 , but high nitrate emissions.
e
Not considering the impact of methane, 23 more effective than CO 2 as GHG.
properties similar to that of other biodiesels. A third thermochemical process,
torrefaction, is similar to pyrolysis, but occurs at lower temperatures, yielding fuels
that are suitable for further use in gasification or combustion, or secondary feedstock
converted into more easily transported and stored forms.
The most used second-generation feedstocks include [11]:
Grass, such as switchgrass, myscanthus, indiangrass, and others, depending on location, as
-
some are more climate adaptable (e.g., switchgrass in the United States, myscanthus in
Southeast Asia).
Jatropha and other seed crops, popular in the early 21st century due to oil returns as high as
-
40%, compared to the 15% of soybeans. Similar seed crops such as cammelina, palm oil, and