Page 52 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 52
Ecofuel feedstocks and their prospects 29
Table 2.8 Amounts of biogas (and methane content) from different feedstocks
Raw material Biogas production (L/kg) Methane content in biogas (%)
Cattle dung 40 60
Food waste 160 62
Fruit waste 91 49.2
Nonedible oil seed cakes 242 67.5
Bagasse 330 56.9
Green leaves and twigs 100 65
Dry leaves 118 59.5
Organic
compounds
(polymers)
Hydrolysis
Monomers
Acidogenesis
VFA
Acetogenesis
Acetic acid CO
H 2 2
Methanogenesis
Biogas
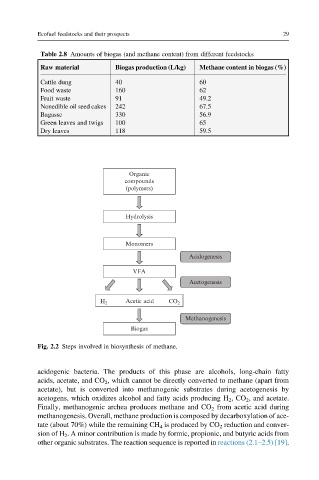
Fig. 2.2 Steps involved in biosynthesis of methane.
acidogenic bacteria. The products of this phase are alcohols, long-chain fatty
acids, acetate, and CO 2 , which cannot be directly converted to methane (apart from
acetate), but is converted into methanogenic substrates during acetogenesis by
acetogens, which oxidizes alcohol and fatty acids producing H 2 ,CO 2 , and acetate.
Finally, methanogenic archea produces methane and CO 2 from acetic acid during
methanogenesis. Overall, methane production is composed by decarboxylation of ace-
tate (about 70%) while the remaining CH 4 is produced by CO 2 reduction and conver-
sion of H 2 . A minor contribution is made by formic, propionic, and butyric acids from
other organic substrates. The reaction sequence is reported in reactions (2.1–2.5) [19].