Page 54 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 54
Ecofuel feedstocks and their prospects 31
Table 2.9 Characteristics of some digestible feedstocks for biogas generation
Type of feedstock Organic content C/N ratio
Animal slurry Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids 3–20
Straw Carbohydrates, lipids 80–100
Grass – 12–25
Grass silage – 10–25
Flotation sludge 65%–70% proteins –
– 30%–35% lipids –
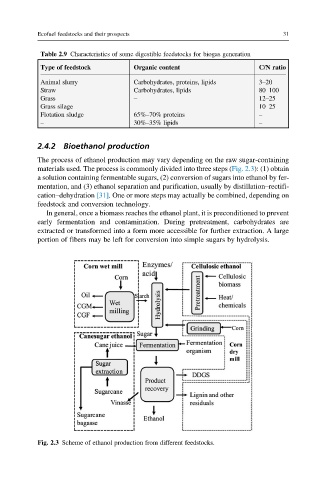
2.4.2 Bioethanol production
The process of ethanol production may vary depending on the raw sugar-containing
materials used. The process is commonly divided into three steps (Fig. 2.3): (1) obtain
a solution containing fermentable sugars, (2) conversion of sugars into ethanol by fer-
mentation, and (3) ethanol separation and purification, usually by distillation–rectifi-
cation–dehydration [31]. One or more steps may actually be combined, depending on
feedstock and conversion technology.
In general, once a biomass reaches the ethanol plant, it is preconditioned to prevent
early fermentation and contamination. During pretreatment, carbohydrates are
extracted or transformed into a form more accessible for further extraction. A large
portion of fibers may be left for conversion into simple sugars by hydrolysis.
Fig. 2.3 Scheme of ethanol production from different feedstocks.