Page 144 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 144
Principles of propulsion 119
gases then pass out through the engine tailpipe,
providing thrust, or can be passed through a
further turbine stage to drive a propeller or
helicopter rotor. For aeronautical applications
the two most important criteria in engine
choice are thrust (or power) and specific fuel
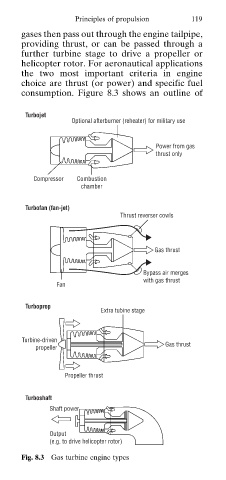
consumption. Figure 8.3 shows an outline of
Turbojet
Optional afterburner (reheater) for military use
Power from gas
thrust only
Compressor Combustion
chamber
Turbofan (fan-jet)
Thrust reverser cowls
Gas thrust
Bypass air merges
with gas thrust
Fan
Turboprop
Extra tubine stage
Turbine-driven
Gas thrust
propeller
Propeller thrust
Turboshaft
Shaft power
Output
(e.g. to drive helicopter rotor)
Fig. 8.3 Gas turbine engine types