Page 146 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 146
Principles of propulsion 121
λ 1.6
Dimensionless specific thrust parameter 1.2 λ = f(P /P ) η = f(P /P ) 0.3 Overall efficiency η 0
2
3
for α = 5
0
3
2
for α = 5
0.8
0.2
0.4
η = f(α)
0
for P /P = 10
3 2 0.1
1 3 7 11 15
Compressor pressure ratio P /P
3 2
2 4 6 8
/t
Cycle temperature ratio α = T 4 0
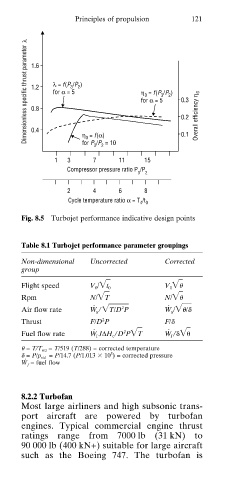
Fig. 8.5 Turbojet performance indicative design points
Table 8.1 Turbojet performance parameter groupings
Non-dimensional Uncorrected Corrected
group
Flight speed V 0 / t 0 V 0
Rpm N/ T N/
·
·
2
Air flow rate W a / T/D P W a / /
2
Thrust F/D P F/
·
·
2
Fuel flow rate W f J∆H c /D P T W f /
= T/T std = T/519 (T/288) = corrected temperature
= P/p std = P/14.7 (P/1.013
10 ) = corrected pressure
5
·
W f = fuel flow
8.2.2 Turbofan
Most large airliners and high subsonic trans
port aircraft are powered by turbofan
engines. Typical commercial engine thrust
ratings range from 7000 lb (31 kN) to
90 000 lb (400 kN+) suitable for large aircraft
such as the Boeing 747. The turbofan is