Page 147 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 147
122 Aeronautical Engineer’s Data Book
characterized by an oversized fan compressor
stage at the front of the engine which
bypasses most of the air around the outside of
the engine where it rejoins the exhaust gases
at the back, increasing significantly the avail
able thrust. A typical bypass ratio is 5–6 to 1.
Turbofans have better efficiency than simple
turbojets because it is more efficient to accel
erate a large mass of air moderately through
the fan to develop thrust than to highly accel
erate a smaller mass of air through the core
of the engine (i.e. to develop the same thrust).
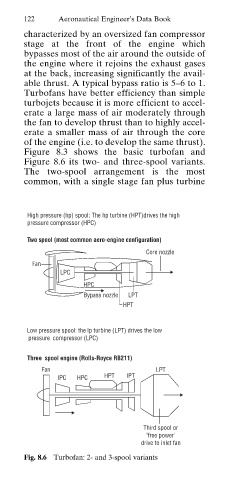
Figure 8.3 shows the basic turbofan and
Figure 8.6 its two- and three-spool variants.
The two-spool arrangement is the most
common, with a single stage fan plus turbine
High pressure (hp) spool: The hp turbine (HPT)drives the high
pressure compressor (HPC)
Two spool (most common aero-engine configuration)
Core nozzle
Fan
LPC
HPC
Bypass nozzle LPT
HPT
Low pressure spool: the lp turbine (LPT) drives the low
pressure compressor (LPC)
Three spool engine (Rolls-Royce RB211)
Fan LPT
IPC HPC HPT IPT
Third spool or
'free power'
drive to inlet fan
Fig. 8.6 Turbofan: 2- and 3-spool variants